Device Features - Front Suspension
Shock absorber support
The front suspension is independent, telescopic, with hydraulic shock absorber struts, coil springs, lower wishbones with braces and a stabilizer bar.
Rice. 4.1. Front suspension assembly: 1 – upper support of the telescopic strut; 2 – upper support cup; 3 – compression stroke buffer with protective casing; 4 – compression buffer support; 5 – suspension spring; 6 – lower spring support cup; 7 – steering rod ball joint; 8 – steering knuckle; 9 – telescopic stand; 10 – eccentric washer; 11 – adjusting bolt; 12 – rack bracket; 13 – steering knuckle; 14 – front brake protective cover; 15 – brake disc; 16 – retaining ring; 17 – wheel hub cap; 18 – splined shank of the wheel drive hinge housing; 19 – guide pin; 20 – wheel hub bearing; 21 – ball joint; 22 – suspension arm; 23 – adjusting washers; 24 – stabilizer strut; 25 – stabilizer bar; 26 – stabilizer bar cushion; 27 – stabilizer bar mounting bracket; 28 – body bracket for mounting the suspension arm; 29 – suspension arm extension; 30 – bracket for fastening the extension; 31 – protective cover of the ball pin; 32 – ball pin bearing; 33 – ball pin; 34 – ball pin body; 35 – suspension strut rod; 36 – outer body of the upper support; 37 – inner body of the upper support; 38 – upper support bearing; 39 – rubber element of the upper support; 40 – travel limiter of the upper support; 41 – protective cap of the upper support
The main element of the suspension is a telescopic, hydraulic shock absorber strut 9 (Fig. 4.1), the lower part of which is connected to the steering knuckle 13 with two bolts. The upper bolt 11, passing through the oval hole of the strut bracket, has an eccentric collar and an eccentric washer 10. When the upper bolt is turned, the camber of the front wheels changes.
The following are installed on the telescopic rack: a coil spring 5, a polyurethane foam buffer 3 compression strokes, as well as the upper support 1 of the rack assembled with a bearing 38.
Rice. 4.2. Telescopic stand: 1 – compression valve body; 2 – compression valve discs; 3 – throttle disk of the compression valve; 4 – compression valve plate; 5 – compression valve spring; 6 – compression valve cage; 7 – recoil valve nut; 8 – recoil valve spring; 9 – recoil valve plate; 10 – recoil valve discs; 11 – throttle disk of the recoil valve; 12 – piston; 13 – bypass valve plate; 14 – bypass valve spring; 15 – plunger; 16 – plunger spring; 17 – rod guide bushing with a fluoroplastic layer; 18 – guide bushing cage; 19 – sealing ring of the rack housing; 20 – rod seal; 21 – oil seal cage; 22 – gasket of the rod protective ring; 23 – rod protective ring; 24 – nut of the strut body; 25 – compression buffer support; 26 – rod; 27 – spring cup; 28 – rotary lever; 29 – rod limit sleeve; 30 – rack body; 31 – cylinder; 32 – drain tube
The upper support is secured with three self-locking nuts to the body mudguard strut. Due to its elasticity, the support ensures that the strut “swings” during suspension movements and dampens high-frequency vibrations. A bearing built into it allows the rack to turn along with the steered wheels. Parts of a telescopic hydraulic shock absorber, shown in Fig. 1, are mounted in the strut housing. 4.2.
A hydraulic recoil stroke buffer is installed in the upper part of the cylinder, consisting of a plunger 15 and a spring 16. It limits the movement of the rod during the recoil stroke.
The lower part of the steering knuckle 13 (see Fig. 4.1) is connected by a ball joint 21 to the wishbone 22 of the suspension. Braking and traction forces are perceived by longitudinal braces 29, which are connected through rubber-metal hinges to transverse arms 22 and brackets 30. At the junction of the brace with the lever and bracket, adjusting washers 23 are installed, which adjust the longitudinal inclination of the turning axis.
A double-row angular contact bearing 20 of a closed type is mounted in the steering knuckle, on the inner rings of which the wheel hub is mounted with interference. The bearing is tightened with a nut on shank 18 of the outer wheel drive joint housing and is not adjustable. All front and rear wheel hub nuts are the same and have right-hand threads.
The anti-roll bar is a bar 25, the knees of which are connected to the transverse arms 22 of the suspension through struts 24 with rubber and rubber-metal hinges. The middle (torsion) part of the rod is attached to the body with brackets 27 through rubber pads.
Features of the “nine” body
Body geometry of the VAZ 2109 As you know, the metal frame of the “nine” is a supporting structure, and the body type is classified as a 5-door hatchback. It is designed on the basis of the G8 body, but is maximally unified, and most of the parts and components have completely different sizes and even shapes. But one thing remains the same for all bodies - they consist of a solid frame and attached components.
VAZ 21099 body geometry and its restoration
The table below provides more detailed information on the VAZ 2109 body and its features.
| Front | Floors | Sidewalls | Roof with wind window frame | Rear | Frame strength elements | Mounted parts |
| Vertical shield, front fender mudguards, cross members, radiator frame panels, front side members, connectors and struts, air intake box, and other small parts. | Front, middle and rear floor panels. The front floor panel is trough-shaped, and in the middle there is a tunnel for exhaust system pipes, pipelines and fuel lines. The tunnel protects them from damage. The rear floor panel has a one-piece stamped niche for a spare wheel. Along the entire floor, side members are welded, which together with the front and rear side members form single hidden longitudinal cavities along the bottom of the entire car. There is good access to both the side members and the hidden cavities. The front, middle and rear cross members, as well as reinforcements and floor extensions are welded to the floor. | The right and left sides of the body consist of outer and inner panels. The outer side panels are made of one-piece parts with central and rear pillars, with side window openings. Internal panels are made integral with the outer wheel arches and with strut reinforcements. The rear sidewalls have reinforcements and on the right sidewall there is a niche for a gasoline vapor separator, as well as grooves and flanges for door seals. To increase rigidity, lower sidewall linings are installed between the lower parts of the outer and inner sidewall panels that form the door sills. Amplifiers are installed at the front and center pillars of the sidewalls. | The wind window frame is made in one piece, to which reinforcements are welded at the top and bottom. The inner windshield frame strut increases the A-pillar's rigidity and creates two isolated cavities. The roof panel has two reinforcements. Two beams with reinforcements for hanging the tailgate are welded to the panel at the back and a front beam at the front. | The rear panel has an upper cross member and is welded to the rear cross member, rear floor and body sides. Tail lights are installed on the rear panel. | Spars and amplifiers | Front fender panels, outer side panels and windshield frame panels, roof panel, rear panel, and outer door and hood panels. |
Replacing silent blocks in the front suspension
Chassis front and rear suspension VAZ 2110 2111 2112 Removing the lever and extension of the front suspension VAZ 2110 2111 2112
Now let’s talk about how to replace the silent blocks of the front levers of the VAZ-2109. For this:
- We hang up the front wheel and remove it;
- Unscrew the fastening of the lever to the ball joint;
- Unscrew the nut securing the stabilizer link and remove it from the lever;
- Loosen the fastening of the lever to the body bracket and remove it from the car;
- The silent block of the front lever of the VAZ-2109 can be removed in several ways - burn it out, knock it out or press it out with a puller or a vice;
- We prepare the hinge seat - clean it of rust and rubber residues with a file. Afterwards, generously lubricate it with soapy water;
- We make a small chamfer on the silent block and center it in the eye of the lever;
- We do the pressing using a vice. We install the lever with the silent block between the jaws of the vice, align the position of the hinge relative to the hole, and then slowly tighten the vice, while periodically checking whether the hinge fits evenly.
- After the silent block bushing rests against the jaws of the vice on both sides, remove the lever and finally seat the hinge in place;
After that, we put the lever on the car. We carry out a similar operation on the other side of the front of the car. After all work, check the tightness of the fasteners. Even if you do all the work yourself, you can complete it in 1 day.
Unusual sounds when moving
If there are certain malfunctions, the front suspension of the VAZ-2109 may make noise or knock. Below are the main causes of problems and recommendations for resolving them.
- If the racks have become unusable, they need to be replaced or repaired.
- The fixing bolts of the stabilizer bar are loose. If the tension pads wear out, the bolts should be tightened and the worn pads replaced.
- Poor quality fastening of the upper support - the problem can be solved by tightening the fixing nuts.
- There is settlement and destruction of the supporting rubber element - it is advisable to replace the problematic part.
- If the lever silent blocks, braces or stabilizer rod struts are worn out, new blocks should be installed.
- The ball joint will need to be replaced if it becomes excessively worn.
- If there is a significant imbalance of the wheels, it is necessary to carry out balancing.
- If a spring or compression buffer breaks, it requires immediate replacement.
What does flat mean when it comes to a car?
An electromagnetic car suspension has been developed – Car Suspension Electromagnet
The concept of “wheel alignment” implies three parameters: camber, toe and caster of wheels.
- Toe refers to the angle between the axis of symmetry of the car and the plane of the wheel. Toe-in is called positive when the wheels are “turned” inward, so to speak, “clumsying.” With negative toe-in, the wheels seem to move apart.
- The angle between the vertical plane and the plane of the wheel is called camber. The camber is positive when the wheels are arranged like a house - the upper part is inclined towards the inside.
- Caster is the pitch angle that is formed when the steering axis is projected onto the longitudinal plane of the car axis.
A true specialist, who has seen sports cars more than once, will first of all ask, for what purpose is the car needed?
- It’s one thing if it’s a so-called “ride” - such cars have become especially popular recently. In this case, it remains to be seen what the specifics of these amateur competitions are - will it be circuit or rally racing, track or sprint. Among other things, you need to decide on the surface - will it be asphalt, soil or snow.
- It’s a completely different matter if the car is used for daily, albeit dynamic, driving around the city. In the first case, more radical tuning options are needed, and everything else, for example, comfort and safety of rubber, becomes secondary.
Let's consider the second option, which assumes that the "eight" will be used every day and it is planned to get maximum pleasure from driving it
In this case, a real specialist pays attention to the castr - the longitudinal angle of inclination. Manufacturers recommend setting the caster at +1 degree
And although we need to listen to the opinions of manufacturers, we will shift this parameter to a value of +3 degrees. This will ensure that the vehicle moves as straight as possible. It will be so stable on the road that the driver can calmly let go of the steering wheel to, say, smoke, without having to be afraid that the car will pull to the side. It should be noted that some athletes go even further, setting the caster to +5 degrees. Setting this parameter becomes possible thanks to changes in the body in relation to the mounting points of the engine and gearbox. But it is always necessary to be guided by common sense, which suggests that such an enhanced parameter will lead to regular replacements of “grenades”. Such a car will not bring much pleasure to every car owner. Thus, caster +3 degrees for a sporty urban G8 is the best option.
It's a completely different matter when you own a Mercedes. On Mercs, the longitudinal inclination is set within 10-12 degrees, because this brand has always strived for straight-line cruising movement thanks to rear-wheel drive.
Experts also pay attention to wheel alignment. The standard option for the “eight” is “zero” with a tolerance of 30 minutes in any direction
In order for the car to behave better when cornering, some suggest turning the camber down to minus for up to 45 minutes. It is important to remember that we are talking about minutes, not degrees!
- Turning to the experience of athletes, we can recall circuit cars in which the camber of the wheels is a complete “house”. A 6-7 degree camber allows you to set the trajectory much better, but in this case the tires will only be enough for one race.
- However, not everyone and not always needs such extreme sports. Also, we must not forget about one more negative point - during intense acceleration, the drive wheels turn inward. In order to understand in practice how this works, you can try riding a motorcycle or even a bicycle, slightly tilting the vehicle. It is not difficult to understand that when tilted, a two-wheeled vehicle always tends to turn in the direction of its tilt. To reduce this “wrapping” effect, it is necessary to adjust one more parameter - toe. The standard value is zero, but in order to compensate for negative camber, positive toe-in of 0.5-1 mm is necessary.
Diagnostics
It would be wisest if you do not wait for a breakdown and diagnose the chassis. There is no consensus on its timing - each specialist has his own opinion on this matter. The mileage recommended for vehicle maintenance varies from ten to thirty thousand kilometers. First of all, you need to focus on operating conditions - if you drive on broken country roads, this figure will be minimal. So:
- The diagnostic procedure includes checking the degree of wear of the shock absorbers. In car services, it is done with a special device that checks the elasticity of the spring. It is impossible to determine the degree of wear visually. Springs that have lost their elasticity may break.
- Be sure to inspect the spring cups, which may also have defects and damage. They check the play in the VAZ CV joint - a torn boot can create problems. Inspection of ball joints and tie rod ends is also necessary.
- Silent blocks are connecting elements between the frame and suspension; due to this worn-out part, the smoothness of the car is lost. Both brake pads and wheel bearings are subject to inspection, and the tightness of the hoses is checked.
- Computer diagnostics makes it possible to identify and promptly eliminate even minor faults, which will protect parts from more significant damage.
- When you fall into a hole or hit a curb, the rims are the first to suffer. The rim of the disc may bend, which will certainly be felt when moving. An iron or cast disk can be rolled, but a forged one cannot be repaired. It will simply burst upon impact.
- The wheels of any car need periodic balancing and checking tire pressure. It must be as prescribed in the operating instructions. When changing wheels seasonally, you need to alternate their installation from the front to the rear axle, which will balance out tire abrasion.
Wheel balancing
If these simple rules are not followed, not only the tires wear out, but also the steering, braking system and transmission elements. Timely maintenance of the chassis is the key to your safety on the road.
Rear suspension VAZ 2109 device, diagram, replacement
A fairly large number of VAZ-2109 owners prefer to repair their car themselves, since the design of the “nine” is distinguished by its simplicity. But before you start working, you must first find the cause of the problem, and, of course, know the sequence of actions.
VAZ-2109 - what the rear suspension consists of
All of the above fully applies to the chassis. Neither the front nor the rear suspensions are complex in design. Accordingly, repairs and troubleshooting should not cause any problems. In this article we will look at the design features of the rear suspension of the VAZ-2109.
First, let's list its elements:
- hub;
- spring and its cups - lower and upper;
- lever mounting bracket;
- shock absorbers and their cushions;
- silent blocks;
- compression progress buffer;
- lever connector;
- rubber gasket;
- beam arm and connector;
- stock;
- spacer;
- support washer.
Generally speaking, the rear suspension of the “nine” is independent, torsion bar. Due to the not very high quality of domestic roads, especially in the outback, it is the chassis that bears the most serious load. Every hole or pothole that a wheel hits is a very noticeable blow to the suspension. You can understand that there are some problems here by hearing. In this case, you will hear an extraneous knock. It can be either deaf or voiced. Experienced professionals use it to make a “diagnosis”, and with very high accuracy. Accordingly, as soon as you hear that something is knocking in the suspension, you should immediately start looking for the problem.
By the way, many car owners strive to improve this component of the car. As a rule, the most common tuning is spacers, which increase the already fairly decent ground clearance. Stock springs and shock absorbers are also often replaced. There are some nuances here. If you change springs, make sure that they have the same stiffness front and rear. However, in this case there is still one exception. The springs at the front may be softer than at the rear, but not vice versa.
When doing such work, you should remember that we are talking about your safety. Accordingly, all installed parts must be of high quality. Products from well-known brands cannot be cheap - otherwise they are fakes, the installation of which can easily result in loss of control of the car while driving.
Another point - when tuning the rear suspension, you don’t need to make it too hard or too soft. In both the first and second cases, this will only bring discomfort to driving. Also, don't lift up the rear too much. It is quite possible that someone really likes this appearance. However, such a design change significantly worsens handling.
Insufficient strut resistance
If the front suspension of the VAZ-2109 has lost the tightness of the return or bypass valve, it is necessary to replace the damaged parts. If there is a small amount or leakage of the working mixture, it is necessary to check, replace worn parts, and add the used composition to the norm.
In addition, in case of wear, settlement, deformation of the guide bushing, rings of the cylinder-piston group, spring mechanism, unusable elements and filters should be replaced and new fluid should be added. It is also necessary to pay attention to the integrity of the additional spring elements, valve discs and hinge block.
DETAILS: Checking the throttle position sensor (TPS) VAZ 2110
VAZ 2109 front suspension diagram
The front suspension of the VAZ 2109 is an independent element of the car, which allows each wheel to work separately from the other. This moment is a very important emphasis in driving a car. Due to this, the VAZ 2109 handles better and feels the road, allowing you to perform complex maneuvers and elements of extreme driving.
The main element of the front suspension of the VAZ 2109 is a telescopic shock absorber strut. There are racks:
- Buttered ones are soft and comfortable. A good choice for bad roads. But on the highway you will be thrown around at high speed.
- Gas - rigid racks. A good choice for highways, highways and roads without holes and potholes. With such struts, the car holds the road well at high speeds.
- Gas-oil ones are something between the two previous racks. Usually they install just such racks, since they are not too hard and soft.
The racks are equipped with coiled springs for rigidity, which also determines your comfort. The top of the strut is secured with 3 bolts along with a support bearing that allows the strut to turn with the car's wheels.
- Shock absorber strut.
- Rod bracket.
- Traction.
- Front lever.
- Spherical bearing.
- Rotary cam.
- Front stabilizer
- Stabilizer bar
The next most important mechanism in the front suspension is the steering cam. Its lower part is connected to a ball joint, which allows us to rotate our mechanism. The top of the steering cam is connected by two bolts to the bottom of the strut. The top bolt allows you to adjust the camber. A thrust bearing is attached to the rotary cam itself, on which the hub is in turn attached.
The anti-roll bar is a rod, which is attached to the car body through silent blocks using a bracket (popularly called crabs), and on the other side to the lower suspension arm.
Front suspension of VAZ 2109 diagram.
- Upper suspension strut support.
- Top cup.
- Progress buffer.
- Buffer support.
- Coil spring.
- Lower spring support cup.
- Ball traction control.
- Rotary lever.
- Shock absorber strut.
- Washer.
- Adjustment bolt.
- Rack bracket.
- The cam is rotary.
- Protective casing.
- Brake disk.
- Retaining ring.
- Hub cap.
- Grenade.
- Guide pin.
- Wheel bearing.
- Ball bearing.
- Lever arm.
- Washers.
- Front stabilizer.
- Stabilizer bar.
- Stabilizer silent block.
- Internal rod bracket.
- Crab. (outer rod bracket)
- Lever stretch.
- Bracket for fastening the brace.
- Silent block of the lever hinge.
- Suspension spacer.
- Stock.
- The upper support housing is external.
- Internal upper support housing.
- Upper support bearing.
- Rubber element for upper support.
- Travel limiter.
- Protective cap.
- Extension joint bushing.
- Stretch joint cushion.
- Washers.
- Stabilizer link joint.
- Rear hinge.
- Ball joint housing.
- Ball bearing.
- Ball pin.
- Protective cover.
Scheme
The diagram below will allow you to determine what components the assembly is divided into and what it represents in the assembly. The table will help you figure out where each suspension element is located.
It is not enough just to know the name and location of the suspension elements. Be sure to understand how the entire system works and how all the components interact with each other.
Replacing rubber joints on the rear suspension
More on how things are changing. First, let's look at how to replace the rear silent blocks of a VAZ-2109. To perform the operation you will need:
- Inspection hole;
- Jacks;
- Tools (key sets, hammer, attachments);
- Bench vice;
- Mount;
- Spring ties;
- Soap solution;
- Pullers for rubber joints;
First, the silent blocks of the rear beam of the VAZ-2109 are replaced. For this:
- We put the car in a pit, jack up the rear on one side, remove the wheel;
- Unscrew the nut of the bolt securing the beam to the body, remove the bolt;
- Using a pry bar, we press the beam down to remove it from the bracket, fix it in this position (by installing a wooden spacer between the beam and the body);
- Using a hammer, carefully knock out the worn hinge;
- Using a device (a long bolt with a nut, two wide washers and a piece of pipe), we press in a new element, having previously generously lubricated the seat and the hinge itself with soapy water;
- We install the beam into the bracket and fix it with a fastening bolt;
After this, the silent blocks of the VAZ-2109 rear pillar are replaced:
- Unscrew the fastening of the rack to the body (top) and beam (bottom);
- We press the beam down so that the stand goes down and the spring relaxes;
- Remove the stand;
- Using a silent block remover, remove the hinge from the rack body (bottom);
- We press in a new silent block using a vice;
- We tighten the springs with ties, then put the stand in place and secure it;
- Remove the ties;
Similar operations are carried out on the other side of the rear of the car. After assembly, you should check the tightness of all fasteners that have become loose. This should be done again after a couple of days of using the car.
Choice
Renault Logan Front Suspension DIY Repair Renault Logan front suspension DIY repair Before you start replacing the silent blocks of the rear beam, you need to decide what exactly you will replace the old, worn bushings with.
We figured out the markings and realized that for the VAZ 2109 you need to take only those that are suitable in size and diameter for the rear beam of the nine.
Today, for the VAZ 2109 they offer two types of silents, differing in the material of manufacture.
| Silent block type | Peculiarities |
| Rubber silent block | They are not as durable, but provide greater softness when operating the car's suspension. |
| Polyurethane silent block | A more rigid modification, in which the increased rigidity is the main disadvantage. At the same time, these products are more resistant to temperature changes, do not deform so quickly, and remain operational longer. |
The choice should be made based on the available budget. Rubber elements cost several hundred rubles cheaper
As for manufacturers, we recommend paying attention to the companies SEVI, BelMag, Boge and SS20
Size difference
Description of design
The front suspension is independent, with telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers, coil springs, lower wishbones with braces and a stabilizer bar.
The basis of the suspension is a telescopic hydraulic shock absorber strut. Its lower part is connected to the steering knuckle with two bolts. The top bolt that goes through the hole in the strut bracket has an eccentric collar and an eccentric washer. By turning this bolt, the camber of the front wheel is adjusted.
The telescopic strut is equipped with: a coil spring, a polyurethane foam compression stroke buffer, as well as an upper strut support assembly with a bearing.
The upper support is secured with three self-locking nuts to the body mudguard strut. Due to its elasticity, the support allows the rack to swing during suspension movements and dampens high-frequency vibrations. A bearing pressed into it allows the rack to turn along with the steered wheels.
Parts of a telescopic hydraulic shock absorber are mounted in the strut housing. If it fails, a repair cartridge can be installed in the rack housing.
The body of the VAZ-2108 rack is slightly longer than the VAZ-2110, so using an externally similar cartridge from the VAZ-2110 is impossible.
The lower part of the steering knuckle is connected to the lower suspension arm through a ball joint. The support is secured with two “blind” bolts. When unscrewing these bolts, be careful: with significant force they often break, so before disassembling, tap their heads in the axial direction.
Braking and traction forces are perceived by longitudinal braces connected through rubber-metal hinges to the lower arms and brackets. At the connection points (at both ends of the brace), adjusting washers are installed for the longitudinal inclination of the steering axis.
A double-row angular contact ball bearing of a closed type is secured in the steering knuckle with two retaining rings. The wheel hub is installed with tension in its inner rings. The bearing is tightened with a nut on the shank of the outer wheel drive joint housing and is not adjusted during operation. The wheel hub nuts are the same, with right-hand threads.
Anti-roll bar - spring steel rod. The ends of the stabilizer are connected to the lower suspension arms through struts with rubber-metal hinges. The middle part of the rod is attached to the body with brackets through rubber pads.
Other causes of malfunctions and possible repairs
Deformation of the suspension elements, especially body braces, disorganizes the wheel angles and makes it impossible to adjust the camber and toe. First of all, you should check the car's silent blocks, rubber cushions, ball joints, and the shrinkage of telescopic struts. Repairing a VAZ-2109 requires replacing rubber cushions and silent blocks if there is rupture and one-sided swelling, including after trimming the end surfaces of rubber elements.
You can check the condition of the front suspension ball joint on the car after removing the wheel, by measuring the distance between the lower arm and the disc element of the brake system. If, after pumping the unit, the distance increases from 0.8 mm or more, the hinge should be replaced.
Replacing the front suspension or repairing it may be necessary due to the following conditions:
- If there is a large difference in tire pressure, this indicator needs to be adjusted.
- Violation of wheel mounting angles - timely adjustment of this unit is required.
- Deformation of the rubber element of the support strut - can be solved by replacing the faulty part.
- If there is a large difference in the elasticity of tires or spring mechanisms, the defective spare part should be replaced.
- In addition, it is necessary to monitor the balancing of the wheels.
To avoid premature repair of the front suspension, it is necessary to follow the recommendations for the maximum load of the vehicle, avoid sudden acceleration and not exceed the maximum permissible values specified in the operating instructions.
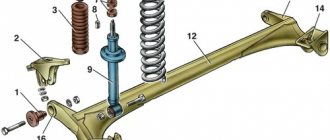
Rear suspension of VAZ 2109
The rear suspension of the VAZ 2109 and its modifications is quite simple. Its design is torsion-lever dependent, that is, the rear wheels are rigidly connected by a beam, which is the main part of the rear suspension. It is on it that all other structural elements are installed. The beam is attached to the car body using rubber-metal hinges, which ensure the movement of the suspension in the vertical plane. This is the oldest type of pendant.
The main design elements of the rear suspension of the VAZ 2109
| 1 | Rear wheel hub |
| 2 | Rear suspension arm |
| 3 | Suspension arm mounting bracket |
| 4 | Rubber bushing for lever joint |
| 5 | Arm joint spacer |
| 6 | Rear suspension arm mounting bolt |
| 7 | Body bracket |
| 8 | Support washer for fastening the shock absorber rod |
| 9 | Upper suspension spring support |
| 10 | Spacer |
| 11 | Suspension spring insulating gasket |
| 12 | Rear suspension spring |
| 13 | Shock absorber rod mounting pads |
| 14 | Compression Progress Buffer |
| 15 | Shock absorber rod |
| 16 | Shock Absorber Protective Cover |
| 17 | Lower suspension spring support cup |
| 18 | Shock absorber |
| 19 | Lever connector |
| 20 | Hub axle |
| 21 | Cap |
| 22 | Wheel hub nut |
| 23 | Sealing ring |
| 24 | Bearing washer |
| 25 | Wheel bearing |
| 26 | Brake shield |
| 27 | Retaining ring |
| 28 | Mud deflector |
| 29 | Control arm flange |
| 30 | Shock absorber bushing |
| 31 | Lever bracket with shock absorber mounting eye |
| 32 | Rubber-metal suspension arm joint |
Looking at the figure, we can distinguish three main components of the rear suspension:
- beam with levers and fastenings
- hydraulic shock absorbers with springs
- hubs
As you can see, the main element is the beam. Levers are welded to it, and brackets with eyes for attaching hydraulic shock absorbers are welded to them. The shock absorbers are fastened with one bolt in the eye of the beam bracket, and are connected to the body by fixing a nut on the shock absorber rod through bushings.
Springs are installed on shock absorbers. For the VAZ 2109 there are two types of springs: class A (hard and high) and class B (less stiff and lower). It is advisable that the car has springs of the same class installed. However, it is allowed to install class A springs on the front suspension, and class B springs on the rear suspension. If you often transport heavy loads in the trunk or in the back seat, then it is better to install class A springs on the rear suspension shock absorbers. This will allow the car to “squat” less when well loaded. It is worth noting that it is prohibited to use class A springs at the front and class B at the rear.
Hubs are attached to the flanges of the beam using four bolts, to which the rear wheels of the car are subsequently attached. The rear suspension hub of the VAZ 2109 has a double-row angular contact sliding bearing, which allows the rear wheels to rotate on their axis.
What problems can there be and how to fix them
The condition of the front suspension should be monitored regularly.
The most common damage is abrasion of the joint covers. These damages are classified as mechanical. Among the malfunctions of this element of the car, unevenness of the lever located on the suspension or on the stabilizer bar is noted. This may result in incorrect and inaccurate operation. In all these cases, you need to check the parts and then simply replace them with new ones. Among the malfunctions there may be minor ones that should be eliminated using a regular repair kit. For example, loosening the bolts of the stabilizer bar or the nut of the support. You should tighten them tighter.
If you hear the suspension making sounds (knocking, creaking), then this indicates more serious damage. First you need to determine where the sound is coming from. You can use a jack for this. Rock the wheel in a vertical plane; if there is a knock in the center of the wheel, then most likely there is a fairly large gap in the bearing. It is better not to change the bearing yourself, as it can be destroyed. It is better to contact a car service center that has special equipment for these purposes.
We draw conclusions: it is better to diagnose and prevent your car and protect yourself while driving than to invest in tuning.
Rear axle
- It is also necessary to adjust the toe and camber here. It is assumed that enough money has been allocated for tuning the car. This means that the rear drum brakes have been replaced by disc brakes.
- It is also possible to install a kind of stand designed to adjust the camber of the wheels. This makes it possible to adjust parameters on the rear axle over a much larger range than can be done on the front. So, the camber can reach -1.5 degrees.
- The rear axle is subject to the same forces as the front. This means that wheel camber will be compensated in the same way as in the case of the front axle - toe, for which its value is set within +2-4 mm.
As an example for comparison, we can take BMW models with traditional rear-wheel drive. The camber of the rear axle is -2.5 degrees, and the toe-in as a compensating factor is +2 mm.
Judging by such a comparison, the improved “eight” will “run” more predictably, quickly, swiftly, even sharply. The car strictly adheres to the required trajectory, the main thing is to ensure reliable adhesion of the wheels to the asphalt. But still there is one “but”...
Firstly, the owner of the G8 now requires greater concentration and attention. In serial VAZ-2108, wheel alignment is adjusted every 10-15 km under normal operating conditions, without replacing suspension parts or special shocks
The maximum mileage between settings in our case is 10 thousand km. Of course, you can drive longer, but we must not forget that these settings are on the verge of common sense. It is also necessary to take into account the condition of domestic roads, which inevitably affect the settings. All this affects the behavior of the car, as well as the condition of the tires. Thus, a strong impact on a hatch or curb stone can lead to a change in caster by 10 degrees and toe by 5 millimeters. This will make it more difficult to turn the steering wheel in place, and the reason for this will be adjustments made without specialists. The consequence of changes in toe and caster can be “oversteer” - the car’s independent “diving” into a turn. Among other things, the above-described settings reduce the vehicle's run-out - when the clutch is disengaged, due to inertia, it travels a shorter distance, unlike the production model. All this means that timely maintenance and checking the wheel alignment settings will extend the life of your car.
- Do-it-yourself tuning of VAZ-2109 and VAZ-2108
- Tuning VAZ 21099 comparison with music
- Different approaches to tuning VAZ 2109 and 2108
- Carbon car wrap
How to check the health of a car's suspension
Perhaps the most critical component after the steering and braking system that influences safe operation is the vehicle's chassis. Therefore, it is necessary to constantly monitor its condition. Of course, in a passenger car, the wear of this unit is not as severe as in a truck, but most often (and VAZ cars are no exception) designers plan for the stability and durability of the suspension scheme taking into account the soft mode.
For a qualified conclusion that the suspension is in good or faulty condition, it is better to contact a service station, where they will be able to fully diagnose the condition of your car on special stands, and the technicians, for whom the suspension diagram has no secrets, will be able to accurately identify a breakdown or minor malfunction. But still, even without knowing the device thoroughly, you need to know the most important symptoms that something is wrong with the machine. It is advisable to pay close attention to the slightest changes in the behavior of the car on the road, which may be symptoms of faulty bridges.
Checking the operation of the support bearing
Due to the fact that the chassis in general and the strut in particular are subject to very heavy loads, the bearing experiences quite large shocks, and it is very important to constantly monitor its condition. The most obvious sign of a bearing failure is a knocking sound coming from the wheel when cornering or overcoming any obstacles. If, after traveling twenty thousand kilometers, the bearing does not raise suspicions, it is still necessary to check its condition in order to understand what to count on in the near future.
History of appearance and purpose
The history of automobile suspension begins with the invention of the first cart, because the axles suspended the body above the ground, which is where the name of this system came from. However, such a suspension device, although it lifted the cart above the ground, transferred to it all the shocks that occurred during the movement of the wheels along the road, which is why the vehicle with a traction of one horsepower turned out to be incredibly shaking. Then, with the development of metallurgy and metalworking, springs appeared, which turned this misunderstanding into something at least vaguely reminiscent of the suspension of a VAZ 2110 car.
Car suspension diagram
Such a cart was much softer, so they began to install springs primarily on passenger versions, that is, various gigs or stagecoaches. Although the harsh impacts on vehicles with leaf springs disappeared, they were far from the comfort of modern cars.
After all, the spring did not dampen the vibrations that occur when the wheel passes over any unevenness, but only made them smoother, in other words, it did not reduce the amplitude of the vibrations, but slowed them down, turning the blow into a smooth push.
The leap in the development of various technologies that occurred at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th centuries led to the appearance of the first shock absorbers, that is, devices that dampen the impact impulse.
As a result, the energy released by the wheel as a result of hitting an obstacle was transformed into a smoothly increasing impulse of noticeably less intensity, that is, the body barely noticeably rose above the road, then smoothly returned to its place. The combination of a spring with a shock absorber led to a sharp increase in driving comfort in cars, significantly differentiating them in this parameter from any carts, including the most expensive carriages.
As the maximum speed of vehicles increased, the capabilities of such a suspension were no longer sufficient, because the higher the speed and the greater the angle of rotation, the stronger the impact of centrifugal force.
When a car turns, centrifugal force tends to throw the car in the direction opposite to the direction of the turn, this is exactly how centrifugal force works. Therefore, the suspension had to compensate for this effect, for which it included various transverse rods that redistribute the force of the centrifugal force.
Therefore, the purpose of the suspension of a VAZ 2110 car or any other vehicle is as follows:
- keep the body at a certain height relative to the ground;
- smooth out shocks that occur while driving over any uneven surfaces;
- reduce lateral roll that occurs when cornering.
A serviceable suspension of VAZ 2108–2115 cars, as well as all modern models, effectively copes with the tasks facing it.
Replacing the lever
The front suspension arm of the VAZ-2109 is one of the most important elements of the unit under consideration. Its replacement is usually carried out in case of a violation of the geometry, after falling into a pothole, hole, ditch, hatch, or when it is impossible to remove the rubber-metal hinges. It is best to repair the VAZ-2109 on a lift, but you can get by with a jack.
First, the front wheel is removed, which should first be hung and secured with a backing made of boards or bricks. The ball nut is unscrewed with a spanner and then removed from the lever. At the next stage, the rear nut is loosened, the stub rack mount and the bracket mount are unscrewed. The bolt is removed, the lever can be freely removed.
The removed front suspension of the VAZ-2109 is inspected for integrity and the presence of defects, after which the rubber-metal hinges or the entire lever are replaced. Assembly occurs in reverse order.
- VAZ 2109 engine injector, cleaning and replacing VAZ 2109 injectors (injector). How to clean or replace VAZ 2109 injectors with your own hands
- Replacing the radiator of the VAZ 2109 stove - Lada master
- Cooling system VAZ 2109 carburetor
- Replacing the pump VAZ 2109 injector
Source Source https://www.vazzz.ru/shema-perednej-podveski-na-vaz-2108/ Source Source https://prometey96.ru/ustrojstvo/perednyaya-podveska-vaz-2109.html
Malfunctions
Here are the main faults:
- cracking or tearing of silent blocks and pillows;
- leakage or loss of shock absorber rigidity;
- punching (loss of rigidity) or breakage of springs;
- wear of the ball joint;
- wear of support bearings;
- separation of brackets from the body;
- poor tightening of threaded connections;
- incorrect castor and camber angles;
- deformation of levers, braces and beams.
Cracking of the rubber filler of the silent block leads to the fact that it can no longer hold the fixing bolt in its place and the lever or beam moves, which leads to displacement of the wheel. At low speeds this is not dangerous, because the driver can compensate for the steering caused by wheel displacement, but at high speeds this often leads to an accident.
A shock absorber that has lost its rigidity does not dampen the movement of the suspension as it should, which is why a ball effect occurs, that is, after passing an obstacle, the wheel bounces several times, losing traction with the road during the ascent, which can lead to a skid.
Squeezing or breaking of springs reduces the vehicle's load-carrying capacity and its ground clearance; in severe cases, the vehicle hits even small bumps with the gearbox or engine protection.
Wear of the ball joint not only leads to spontaneous rotation of the wheel, but can also cause the strut to come off the lever and the machine on this side to fall to the ground.
Damaged support bearings accelerate tire wear and also damage the seat in the body (cup). Severing the brackets from the body makes the suspension ineffective and it is impossible to drive such a car.
Poor tightening of threaded connections leads to the nut being unscrewed, after which the bolt falls out of its place and the suspension triangle is broken, so such a car can only be moved by a tow truck.
Incorrect castor and camber angles, as well as deformation of the levers, braces and beams, change the behavior of the car when turning, which is not too dangerous at very low speeds, but at least at medium speeds (60–90 km/h) poses a serious threat.
Signs of wear or damage to the undercarriage
- Leaks under the car in the area where suspension parts are located. Cars of the VAZ 2109 model, as a rule, already have a long service life (and the design of the hydraulic cylinders is designed for a certain resource, which they may have exhausted a long time ago). There is a high probability that the oil seal or shock absorber rod mirror may wear out, so pay attention to possible leakage of hydraulic fluid (in principle, you need to be careful about any leaks from the car);
- Knocking when driving, yawping along the road is the most common sign of a malfunction. As a rule, this indicates wear or loosening of the components; carefully inspect the suspension, or best of all, contact a workshop;
- When acting on the suspension (try pressing on the hood or, conversely, lifting your car, experienced auto mechanics, when first getting acquainted with passenger cars, not only the VAZ 2109, roughly assess the condition of the chassis), the suspension does not provide sufficient resistance - the first sign of malfunction hydraulic cylinders. There can be many reasons - insufficient amount of fluid, leakage due to wear of the seals, fluoroplastic bushing, wear of the rod, malfunction of the valve mechanism. It is necessary to replace worn parts, replenish the oil in the cylinders, or eliminate the malfunction of the valve mechanism;
- When driving (especially on uneven roads), hard shocks with a characteristic sound occasionally appear, which can even be felt on the steering (the so-called “breakdown” of the suspension). The appearance of this symptom indicates that the springs (most often the rear chassis) have lost their properties due to metal fatigue; hydraulic shock absorbers may also not work properly. In any case, it is necessary to inspect the structure of your suspension and make repairs.
DETAILS: Adjusting the clutch cable VAZ 2110
We have not yet mentioned the uneven
- if your wheels are adjusted for wheel alignment and balanced, and the CV joints (since the VAZ 2109 is assembled according to a front-wheel drive system) work correctly, then the reason is the chassis, there is a breakdown somewhere, excessive play or wear.
In conclusion, it should be noted that although the chassis of the VAZ 2109 is not subject to such overloads as a similar truck unit, its design is still quite complex and requires constant attention; fortunately, the suspension design allows for maintenance and repair without large material costs.