How to properly bleed the brakes
Before starting work, you should make sure that you have the necessary materials and tools that should be on hand:
- brake fluid;
- wrench “8” (socket or open-end) to loosen the fittings;
- elastic hose suitable for a tight fitting on the fitting;
- a suitable container for receiving used brake fluid;
- slotted screwdriver;
- wheel chocks;
- lift, inspection pit or overpass.
A partner, sitting in the cabin, will press the brake on command.
Sequencing
Hang the car on a lift or secure it with wheel chocks on a viewing hole or overpass. Wheel bleeding procedure:
- Rear right wheel.
- Front left wheel.
- Rear left wheel.
- Front right wheel.
The algorithm of actions performed is the same for all four wheels.
Leveling procedure
Bleeding the Kalina brake system will require you to first take the following preparatory steps:
- Open the electrical circuit of the low brake fluid level indicator sensor in the expansion tank.
- Unscrew the cap and remove it together with the float, freeing the neck to quickly replenish the volume of fluid in the braking system during adjustment.
- Make sure that the level is above the MIN mark, top up if necessary.
- Check that the pressure regulator valve is set correctly (otherwise it will not be possible to bleed the rear wheels).
Self-bleeding brakes
In the future, you cannot do without an assistant who, sitting in the driver’s seat, will operate the brake pedal according to the commands of a partner located under the bottom of the car. The procedure for pumping wheels on Kalina is as follows:
- The protective cap is removed from the fitting and its tip is covered with an elastic tube. The mating part of the tube is placed in a suitable container.
- Using a ring wrench “8” with a slot, the swivel nut of the fitting is covered.
- The person in the cabin, upon command, presses the brake pedal all the way with successive movements and holds it close to the floor.
- A partner under the car unscrews the fitting counterclockwise and, after waiting for the brake fluid to stop leaking, closes it again.
The last two steps are repeated until air bubbles stop appearing in the liquid. Having put the safety cap on the screwed fitting, they begin to work with the next wheel according to the scheme.
Fluid control
Constantly monitoring the level of brake fluid in the expansion tank above the minimum mark will help eliminate the occurrence of air locks in the system.
Design features of Lada Kalina brakes
The car is equipped with two braking systems - working and parking.
The service braking system is designed to reduce the speed of the vehicle, up to its complete stop and briefly hold the vehicle stationary.
The service brake system is dual-circuit, diagonal, hydraulically driven, and consists of a master cylinder with a vacuum booster, four wheel brakes and a fluid pressure regulator in the rear brakes.
The front wheel brakes are ventilated discs, the rear wheels are drum brakes.
Each of the car’s circuits includes brake mechanisms for two wheels: one front and one rear, located diagonally on the car.
One circuit includes the brake mechanisms of the front right and rear left tracks, and the second circuit includes the brake mechanisms of the front left and rear right tracks.
If one circuit fails, the second circuit, albeit with less efficiency, will ensure the vehicle stops.
The fluid pressure regulator limits the flow of fluid to the rear brake mechanisms when there is insufficient load on the rear axle, thereby preventing the rear wheels from locking and the rear axle of the vehicle from skidding during sudden braking.
The regulator body has a control hole closed with a plastic plug. Liquid leakage from this hole indicates leakage of the regulator rings.
To reduce the force applied by the driver to the brake pedal, a vacuum booster is installed in the brake system drive, which operates due to the vacuum generated in the intake manifold of a running engine.
A brake fluid reservoir is installed on the brake master cylinder body.
A sensor for insufficient brake fluid level is built into the lid of the bank.
If the liquid level in the tank drops dangerously, the sensor turns on the warning lamp on the instrument panel.
Some vehicles are equipped with an ABC (anti-lock) braking system.
Payment via PayPal
After selecting payment via PayPal, the PayPal payment system will launch, where you need to select the payment method: bank card or PayPal account.
If you already have a PayPal account, then you need to log into it and make a payment.
If you do not have a PayPal account and you want to pay using a bank card via PayPal, you need to click on the “Create an Account” button - shown with an arrow in the picture.
PayPal will then prompt you to select your country and provide your credit card information.
After specifying the information required to make the payment, you must click on the “Pay Now” button.
basic information
The braking system controls the speed of the car, its stopping, and also keeping it in one position using the braking force that occurs between the road and the wheels of the car. The stopping force can be created by the car engine, the car wheel stopping mechanism, or an electric or hydraulic retarding brake, which is located in the box. Two types of braking systems are immediately installed on the Lada Kalina car, such as:
- Working brake system. This type of system is used at any speed of the machine to completely stop or reduce the speed. At the same time, it begins to work immediately after pressing the brake pedal. This type is considered the most effective in comparison with other types.
- Parking brake system. It is necessary to keep the machine in place for a certain time. In other words, thanks to it, the possibility of the car moving without the driver’s knowledge is completely eliminated.
Malfunctions of the braking mechanism
The main task of diagnosing a car is to detect malfunctions in the Lada Kalina braking mechanism, as well as eliminate them with the least possible use of foreign currency. In addition, timely detection of defects in the braking system will allow you to avoid huge financial expenses, so how can you prevent breakdowns. In specialized centers, diagnostics (the process of establishing a diagnosis, that is, a conclusion about the nature of the disease and the patient’s condition)
It is carried out on a special shield, but you can do it yourself at home. To determine the malfunction, you must pay close attention to your own vehicle.
So, let's look at the main malfunctions of the Lada Kalina braking system?
- The cylinders on the trailer are not completely filled. Most often, such a malfunction occurs due to a breakdown of the trailer brake control units.
- The air cylinders of circuits 1 and 2 are not completely filled. The reason may be clogging of the pipelines and triple valve, as well as lack of clearance in the triple safety valve.
- The air cylinders of circuits 3 and 4 are not completely filled. This may be due to a clogged pipeline or damage to the double safety valve.
- Oil getting into pneumatic systems. In this case, it will be necessary to check the piston rings, as well as the compressor cylinders.
- Air tanks fill slowly. The main reason for this malfunction occurs due to the formation of various cracks and damage to the cylinder.
- Very high or very low pressure in the air cylinders of the 1st and 2nd circuits. In this case, it is necessary to adjust the pressure regulator and also check the functioning of the two-pointer pressure gauge.
- The spare and parking brakes are faulty. The cause of the malfunction may be a breakdown of the accelerator valve, the emergency brake release valve, a large stroke of the chamber rods, or an incorrectly installed brake valve regulator drive.
- The brake pedal does not work. The reason may be a poorly adjusted brake valve, a broken pressure limiting valve or a brake valve, an incorrectly installed brake valve regulator drive, or a large stroke of the brake chamber rods.
- Unreal braking. Such a breakdown may be associated with a malfunction of the pneumatic valve, with a breakdown of the dampers or solenoid valve.
- The car cannot be removed from the spare or parking brake. Such a malfunction may be associated with an air leak from the third circuit, a breakdown of the stubborn bearing of the energy accumulator, or a breakdown of the atmospheric outlet of the accelerator valve.
Most often, the reason for problems with the Lada Kalina braking mechanism is an untimely change of brake water, and this can lead to complete brake failure.
It needs to be changed frequently due to the fact that at the time of use it absorbs all the water. There may also be a missing level of brake water, because it evaporates during boiling, which occurs when the vehicle stops.
Source: autodont.ru
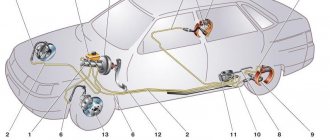
The brake system of the Lada Kalina car
The hydraulic brake system of a VAZ 1118 car consists of a pedal lever, a hydraulic master cylinder, a vacuum brake booster 1118, a hydraulic reservoir, a pressure regulator, a regulator drive lever, pipelines, flexible reinforced rubber hoses, tees, and fastening clamps. At the same time, the brakes on this VAZ model can be equipped with an anti-lock braking system, but it was not installed in the first series of Kalina production. Today, almost the entire line of cars comes with an ABS system.
Vacuum booster on a VAZ 2170 2171 2172 Lada Priora: 1 - tip mounting flange; 2 — rod; 3 — diaphragm return spring; 4 — sealing ring of the master cylinder flange; 5 - main cylinder; 6 — amplifier pin; 7 — amplifier housing; 8 - diaphragm; 9 — amplifier housing cover; 10 - piston; 11 — protective cover of the valve body; 12 — pusher; 13 — pusher return spring; 14 — valve spring; 15 - valve; 16 — rod buffer; 17 — valve body; A - vacuum chamber; B - atmospheric chamber; C, D - channels
Features of the front wheel braking system
The front wheels of the VAZ 1118 are equipped with a ventilated disc system with a piston floating caliper. It includes a wheel cylinder and a caliper, which are tightened together with special screws. The cylinder itself is attached to the guide pins with two bolts installed in the guide block (holes). The pads are pressed against the guide grooves by springs. Inside the cylinder there is a piston with a sealing ring having a rectangular cross-section. The elasticity of the ring provides an optimal gap between the disc and the brake pads, which ensures high-quality functioning of the system.
Front wheel brake mechanism on a VAZ 2170 2171 2172 Lada Priora: 1 - brake disc; 2 — pad guide; 3 - caliper; 4 — protective casing; 5 - working cylinder; 6 — brake hose; 7 — air release valve; 8 - guide pin; 9 — protective cover of the guide pin; 10 — brake pads
Features of the rear wheel braking system
The brake system of the Lada Kalina, the design of which significantly increases its safety, is distinguished by its thoughtfulness and high reliability. The rear wheels of Kalina are of the drum type, with a two-piston wheel-type cylinder, as well as automatic adjustment of the clearance space between the drum and the block. A drum brake consists of the drum itself, shoes, hydraulic cylinder, tension springs, protective disc, retainer and shoe spacer.
Rear wheel brake mechanism on a VAZ 2170 2171 2172 Lada Priora: 1 - rear brake pad; 2 — parking brake drive lever; 3 — lower tension spring of the pads; 4 — brake mechanism shield; 5 — parking brake cable; 6 — front brake pad; 7 — guide spring; 8 — expansion bar; 9 - working cylinder; 10 — upper tension spring of the pads; 11 — finger of the parking brake drive lever
Function of the braking system
It is important to note that only the smooth functioning of all elements of the device ensures safety and reliable deceleration of the vehicle.
The brake system of the Lada Kalina operates as follows: when you press the brake pedal, the piston, moving in the cylinder, displaces fluid through the main outlet valve into the brake hydraulic system hose. The fluid moves through pipelines to the main wheel mechanisms, which helps move the pads to the discs in the front wheels, and the rear ones to the drums. When contact occurs, braking begins, and the angle of change of the pedal lever affects the speed of deceleration of the car.
Parking brake and its device
In addition to the main brake system, mention should be made of the parking brake, which has a standard mechanical configuration and consists of an adjusting rod, a lever, two cables, an equalizer, spacer bars, and pad drive levers. The parking brake system of the VAZ Kalina is driven by the brake mechanism of the rear pads, which ensure reliable fixation of the car from accidental movement.
It is important to remember that a properly configured brake should ensure vehicle immobility on a slope of up to 23% when empty, and up to 19% with a full load.
Principle of operation
The main criterion is that all elements of the Lada Kalina braking system must function clearly, which guarantees the safety and reliable braking of the vehicle.
The operating principle of the Lada brake system is as follows. After pressing the brake pedal, the piston begins to move in the cylinder. Fluid from the main exhaust valve enters the Kalina brake system through hydromechanical hoses. The fluid is then directed towards the main wheel mechanism through pipelines, creating the necessary conditions for the movement of the pads to the front wheel disks and to the rear drums. Contact occurs and braking occurs.
Repair work: debugging the brake system
If the following problems are detected, it is recommended to immediately contact a car service to eliminate them.
- Presence of air in the system. You can solve the problem not only with service, but also yourself. To do this, you need to bleed the brakes.
- Brake fluid leaking. This situation indicates a malfunction of pipelines and rubber hoses.
- Increasing pedal stroke. The problem that has arisen indicates a problem with the vacuum booster. It is recommended to replace the hose and check its attachment points.
- Reduced braking efficiency. In this case, the reason may be oily brake linings, jammed cylinder pistons, compromised gasket integrity, or defective adjustment by the regulator.
- Squeaking or vibration when braking. Perhaps the tension spring is weakened, the linings are out of order, or the rubbing linings are oily.
Downloading a book
After successfully completing the payment (by any method) and returning to the KrutilVertel store from the payment system website, you will be taken to the successful payment page:
The book you purchased will be in your personal account, from where you can always download it.
Please note that after making the payment, you need to return back from the payment system website to the KrutilVertel website. If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book
If for some reason you did not return back to the site and closed the payment system tab with a message about the successful completion of the payment, please let us know - we will send you a letter indicating access to download the book.
Checking the pedal free play
Free travel of the brake pedal is the pedal travel from its top position until the brakes begin to operate. It should be 3-5 mm.
To complete the work you will need a ruler or tape measure.
1. Prepare the car for work.
2. Place a ruler or tape measure near the pedal and measure the distance from the floor to the outer surface of the brake pedal.
3. Pressing the pedal with your hand, lower it until we feel an increase in resistance to the movement of the pedal.
We repeat the measurements. Based on the difference in acquired values, we determine the free move.
The presence of free travel of the brake pedal ensures that after stopping braking, the pistons of the head brake cylinder return to their initial position, and as a result, there is no excess pressure left in the hydraulic brake drive. When the brake light switch is set so that it limits the brake pedal travel back, the brake system will be able to maintain pressure at which the brake pads will constantly apply the brakes.
If the free travel of the brake pedal is less than a rational value, you need to adjust the position of the brake signal switch. Increased free play of the brake pedal may be caused by play in the drive mechanism. Worn parts need to be replaced. Also, a prerequisite for the malfunction may be the presence of air in the hydraulic brake drive or a malfunction of the head brake cylinder. The identified malfunction must be removed.
Features of front and rear wheel brakes
The front wheel brake mechanism is made in the form of ventilated discs with a single-piston floating clamp. This clamp includes the caliper and wheel cylinder, which are tightened with screws. The cylinder is attached directly to the guide pins using two bolts.
The bolts are placed in the passages of the guide blocks, pressed by the guide spring grooves. A piston with a sealing ring of rectangular cross-section is placed inside the cylinder. This ring provides the most rational distance between the disc and the brake pads. This organization of Kalina's braking system contributes to its efficient functioning.
Replacing the brake drum
The rear brakes are drum type. They consist of a two-piston hydraulic wheel cylinder, a drum, shoes, tension springs, a protective disk, shoe spacers and an automatic distance regulator from the drum to the shoes.
In addition to the head system, the developers equipped the Lada with a mechanical parking brake, which is driven by the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels.
The parking brake system includes:
- adjusting rod;
- lever arm;
- two cables;
- equalizer;
- spacer bars;
- pad drive levers.
Checking the brake water level
The brake water level is checked from time to time: once a day during the operation of the vehicle, during any maintenance, after performing operations to bleed the hydraulic drive of the brake system and replace the brake water, when the warning lamp on the device panel lights up, signaling an insufficient level of brake water in the head brake reservoir cylinder.
1. Prepare the car for work.
2. Use a rag to remove dirt from the head brake cylinder reservoir.
3. Visually check the brake water level in the reservoir. It should be between the MIN and MAX marks on the tank body.
4. Check the degree of wear of the brake pad linings of the front and rear brake devices.
5. If the wear of the brake pads is within normal limits, and the water level in the reservoir is below the MIN mark, then disconnect the tip of the wiring harness from the brake water level emergency drop sensor, unscrew and remove the reservoir cap.
6. Add new brake fluid to the reservoir up to the MAX mark (when installing the reservoir cap, the sensor float will be immersed in the liquid and its level will increase).
7. Close the tank lid tightly.
8. Connect the wiring harness block to the sensor connector.
9. Check the operation of the emergency brake water level sensor: with the ignition on, press the rubber lining of the reservoir lid from above. If the sensor is working properly, the warning lamp on the device panel will light up.
Payment via PayPal
After selecting payment via PayPal, the PayPal payment system will launch, where you need to select the payment method: bank card or PayPal account.
If you already have a PayPal account, then you need to log into it and make a payment.
If you do not have a PayPal account and you want to pay using a bank card via PayPal, you need to click on the “Create an Account” button - shown with an arrow in the picture.
PayPal will then prompt you to select your country and provide your credit card information.
After specifying the information required to make the payment, you must click on the “Pay Now” button.
How does the Kalina brake system work?
Braking is carried out by transferring force from the vacuum brake booster through two circuits to the brake cylinders with simultaneous automatic adjustment depending on the load on the rear wheels. The front-wheel drive is equipped with disc brakes, and the rear-wheel drive is equipped with drum brakes.
Brake system "Kalina" - diagram
The braking system of this machine is formed by the following components:
- brake pedal;
- vacuum booster;
- brake master cylinder block with expansion tank;
- two separate circuits for transmitting force hydraulically to the brake pads;
- pressure regulator in the circuit to set the braking mode of the rear wheels.
Pressure on the brake pedal is amplified by the system and transmitted to the wheels. The circuits operate on a cross principle - one circuit is responsible for braking the left rear and right front wheels, the other - the right rear and left front.
In this way, the duplication function is implemented in the event of a sudden failure or malfunction of one of the circuits. The remaining working circuit is capable of providing braking to the vehicle.
For a more even distribution of forces, the rear wheels are equipped with an automatic pressure control device depending on the load on the rear axle. As the load increases, the force applied to the brake pads increases proportionally. The operation of the regulator is controlled by a special lever that sets the gap, after overcoming which the system for redistributing the braking force between the front and rear pairs of wheels is activated.
Brake system equipment
- Brake pedal. This is a hanging type part. There is a spring return mechanism. Just above the pedal part, the developers placed a brake signal switch.
- Vacuum reinforcement is a part of the diaphragm structure. It is designed to reduce the force exerted by the driver when pressing the brake pedal. It operates due to the difference in pressure in vacuum and atmospheric tanks.
- Fluid pressure regulator. Installed in systems without anti-lock wheels. Serves as a limiter for the flow of fluid towards the rear brakes when the vehicle is partially loaded. This element prevents the wheels from locking and prevents the rear of the vehicle from skidding.
- Brake fluid height sensor. Indicates a drop in liquid height below the minimum value. It is located in a plastic tank, attached through the upper passages of the cylinder using rubber bushings. After the brake fluid level drops below the permissible level, the sensor transmits a signal to the light on the instrument panel.
- Brake signal switches. Their operation is as follows: after pressing the pedal, the electrical contacts close.
- Main brake cylinder. Attached with two studs to the vacuum booster. A reservoir for brake fluid is attached to the base of the brake cylinder.
- Pipelines.
- Regulatory drive lever.
- Elastic reinforced rubber hoses.
- Tees.
- Fastening clamps.
Problems when paying with bank cards
Sometimes difficulties may arise when paying with Visa/MasterCard bank cards. The most common of them:
- There is a restriction on the card for paying for online purchases
- A plastic card is not intended for making payments online.
- The plastic card is not activated for making payments online.
- There are not enough funds on the plastic card.
In order to solve these problems, you need to call or write to the technical support of the bank where you are served. Bank specialists will help you resolve them and make payments.
That's basically it. The entire process of paying for a book in PDF format on car repair on our website takes 1-2 minutes.
If you still have any questions, you can ask them using the feedback form, or write us an email at
Checking brake pad wear
We check the degree of wear of the brake pads of the front brake devices in the following sequence.
1. Install the car on the inspection ditch.
2. Remove the front wheels.
3. When checking the pads of the left brake mechanism, turn the steering wheel completely to the left, and when checking the pads of the right brake mechanism, turn it to the right.
4. Through the inspection hole in the movable caliper bracket, we visually determine the thickness of the brake pads.
If the thickness of the lining of at least one pad is less than 1.5 mm, we change all the brake pads of the brake devices of the right and left wheels.
5. At the same time, we check the mobility of the brake cylinder pistons. If the piston becomes sour, replace the cylinder.
To check the degree of wear of the rear brake pads, you will need a flashlight.
1. Prepare the car for work.
2. Using a slotted screwdriver, remove the rubber plug for the inspection hole in the support shield of the rear wheel brake mechanism.
3. Light the inspection hole with a flashlight. If the thickness of the brake pad lining “ A ” is less than 1.5 mm, change all the brake pads of the brake devices of the right and left wheels.
4. Install the plug into the space.
General checks
Brake Line Connections
Check the condition of the service brake system and parking brake components.
Brake Line Connections
Leakage of brake fluid in connections and hydraulic drive is not allowed.
Parking brake tensioner locknut
The full travel of the parking brake lever should be 2-4 teeth of the sector ratchet device, adjust if necessary:
Move the parking brake lever to its lowest position, loosen the locknut of the tensioning device and, by tightening the adjusting nut, tighten the cable so that the stroke of the lever along the sector ratchet device is 2-4 teeth (clicks).
Checks while driving
Check the effectiveness of the service and parking brakes.
Check the operation of the vacuum brake booster. With the engine not running, press the brake pedal 5-6 times, holding the pedal pressed, and start the engine. If the amplifier is working properly, the pedal should “move forward” after starting the engine. If the pedal does not “go forward”, it is necessary to check the attachment of the tip, the condition and fastening of the vacuum booster vacuum hose, and if necessary, tighten the tip and hose clamp.
Service
Maintenance consists of inspecting all components and replacing them in case of wear. All service looks like this:
- checking the brake pedal travel;
- checking and possible adjustment of the parking brake (Kalina has a handbrake from “nine”, so it must be tightened often);
- inspection of all tubes and hoses;
- inspection of the condition of brake discs, drums and pads;
- checking the brake fluid level and replacing it approximately every 40 thousand kilometers.
Maintenance of the brake system must be carried out every 10 thousand kilometers.
Problems when paying with bank cards
Sometimes difficulties may arise when paying with Visa/MasterCard bank cards. The most common of them:
- There is a restriction on the card for paying for online purchases
- A plastic card is not intended for making payments online.
- The plastic card is not activated for making payments online.
- There are not enough funds on the plastic card.
In order to solve these problems, you need to call or write to the technical support of the bank where you are served. Bank specialists will help you resolve them and make payments.
That's basically it. The entire process of paying for a book in PDF format on car repair on our website takes 1-2 minutes.
If you still have any questions, you can ask them using the feedback form, or write us an email at
Checking the vacuum brake booster
1. We prepare the car for work.
2. With the engine not running, press the brake pedal a couple of times until the hissing in the brake booster stops.
3. Press the brake pedal and hold it pressed.
4. Without releasing the pedal, we start the engine.
5. If immediately after starting the engine the pedal moves down a little, the brake booster is working properly.
If this is not the case, we check the integrity of the vacuum supply hose to the vacuum booster, the tightness of its connection to the inlet receiver and the booster return valve branch pipe. If the hose is intact and connected tightly, the vacuum booster is faulty.
Differences in the brake system of the Lada Kalina Sport
Kalina Sport is an improved version of the Lada Speed. Kalina characteristics of this model are significantly braking. The Kalina Sport system has also undergone changes during modernization of the car. The rear wheel brakes were replaced with disc brakes. On Kalina Lada Sport, an anti-lock braking system is installed exclusively on the wheels. This eliminates the possibility of the car skidding.
The use of high-quality spare parts affects many factors. It is recommended to use original factory spare parts. It is better to carry out adjustment and repair work at specialized technical points. brake maintenance is a guarantee of the safety of all road users
Attention to the brake system will ensure its longevity. The operation of the entire machine depends on this.
Main problems with the brake system of the VAZ 1118 Kalina
Everyone understands the importance of this system in a car, and therefore timely maintenance can significantly improve safety and also prevent accidents. At the same time, during intensive use, as well as the specificity and quality of the components in the mechanism, some of its elements may fail ahead of schedule.
That is why you should constantly monitor its condition, and also pay attention to possible malfunctions.
- Air in the brake system. To solve the problem, you need to “bleed” the system, which can be done both in a garage and at a service station.
- Brake fluid leak. Worn pipelines and rubber hoses
- Increased pedal travel. The vacuum booster is faulty; the hose needs to be replaced or its attachment to the fittings checked.
- Low braking efficiency. It is possible that the brake linings become oily, the pistons in the cylinders become jammed, the linings wear out, or the regulator is adjusted incorrectly.
- The car pulls to the side during braking. Different tire pressures, wheel camber/toe angles are incorrect, disks or drums are dirty or oily.
- Brake vibration or squeaking. Weakening of the tension spring, wear of the linings, oiling of the friction linings.
Features of the brake system of the Lada Kalina Sport
Lada Kalina Sport is an improved version of the domestic car, which has higher speed characteristics. As for the brakes, they have been qualitatively improved - the rear drum units have been replaced with disc ones.
In general, the Kalina Sport brake system is more reliable, since it is designed for high loads and speeds higher than usual. In addition, an ABS anti-lock braking system is installed here, which provides additional protection against skidding.
In conclusion, it should be said that a lot depends on the quality of the spare parts used, therefore, when repairing or undergoing maintenance, it is best to give preference to original spare parts. In addition, all work on adjusting, replacing or upgrading the brake structure should be carried out exclusively at a certified service station.
Only high-quality repairs will ensure the safety and durability of your car!
Yesterday my friend arrived, for whom we recently bought a Kalina sedan. So, his problem was the following: fluid began to quickly leave the brake reservoir. I looked at all the wheels, hoses and cylinders, but everything was fine there, and no leaks were found. Then I looked closely at the bottom of the tank, where it enters the main cylinder, streaks were visible.
In general, we decided to remove the tank, since it was not really clear whether the problem was in it, or in the rubber bands themselves. To remove it, you will need to disconnect and remove the battery, so you will need:
- keys for 10 and 13
- a flat-head screwdriver or a hammer (more precisely, you need the handle of a hammer to use it as a lever)
- syringe for pumping liquid out of the tank
So, first of all, disconnect the terminals and remove the battery. After this, unscrew the plug and remove it together with the float, and also disconnect the plug from the hood end switch by pressing the latch:
Then, using a syringe, pump out the brake fluid as much as possible. Now comes the most difficult part: removing the reservoir from the rubber seals of the master brake cylinder. You can use either a large flat-head screwdriver, prying it from below, or, even more conveniently, the handle of a hammer, using it as a lever. You should pry it off carefully so as not to break off the tank, otherwise the fittings may remain in the cylinder. The photo below shows the places where you should apply force during removal, that is, pry:
Also note that you will need to bend back the plastic clips that secure the tank to the cylinder:
As a result, I had to try a little to remove the tank without damage, since it sits quite tightly in the elastic bands.
Then we called another friend to buy us a tank specifically for Kalina, since it does not fit other VAZ models. But the seller, as I thought, sold him the eight, saying that they were the same. As a result, they went to get the tank again and after that we finally installed everything. There is no need to pump the brakes after performing this work, since the fluid remains in the master cylinder up to the very edges of the rubber bands.