VAZ 2107 clutch: device
The “Seven” has a dry single-disc clutch. The clutch hydraulic master cylinder is located directly under the pedal, when pressed, the pusher moves, acting on the master cylinder piston, creating pressure. The brake fluid that fills the hydraulic drive is squeezed out and flows into the working cylinder.
The piston of the working cylinder is connected to the clutch fork by a pusher. When you press the pedal, the latter moves the fork, it displaces the release bearing and separates the support and pressure discs. As a result, the torque from the crankshaft flywheel is no longer transmitted to the gearbox and it becomes possible to change gear.
If the clutch unit malfunctions, when you press the pedal, the gearbox shaft continues to rotate and changing gears becomes difficult or even impossible. If the clutch is adjusted incorrectly, the discs may slip, which is accompanied by accelerated wear.
You cannot continue to drive a car with a faulty clutch - both the clutch discs and the gearbox may be damaged. Therefore, at the first sign of a malfunction, you should start repairing and adjusting it.
General information
In order for the replacement of the VAZ 2107 clutch slave cylinder to be justified, it is good to know its purpose and the first signs of a malfunction. The torque transmission system on classic VAZ models is driven by a hydraulic drive, the main task of which is to transmit force when pressing the clutch control pedal.
In turn, the hydraulic drive consists of two cylinders: the main and the working. When the pedal is applied, pressure is created in the main center, as a result of which the brake fluid is pumped through the valve into the working cylinder (WC). The latter activates the rod, which squeezes the fork, thereby selecting gears.
Replacing the clutch master cylinder VAZ 2107
The simplest way to repair a VAZ 2107 clutch is to change the worn cylinders (main and slave). Their price is low, and the labor intensity of the operation is much lower than when carrying out repairs. Therefore, car owners often prefer to replace rather than repair clutches.
Let's start by replacing the master cylinder. The order of operations is as follows:
- Drain the brake fluid from the clutch reservoir into another container. This can be conveniently done using a syringe.
- Loosen the clamp and remove the hose from the master cylinder fitting.
- Unscrew the fitting of the metal tube going from the master cylinder to the slave cylinder and disconnect the tube.
- Using a 13mm wrench or a socket with an extension, unscrew the two nuts securing the master cylinder to the body bulkhead and remove the master cylinder.
The new clutch master cylinder can now be installed. Before doing this, you should check the condition of the flexible hose of the clutch reservoir. If it cracks at the end, it needs to be trimmed slightly or replaced with a new one.
When installing a new cylinder, it is necessary to ensure that the clutch pedal drive rod fits inside the cylinder. For convenience, you can ask your partner to slightly press the clutch pedal and hold it. Then follows:
- Install the master cylinder onto the studs and tighten the nuts.
- Attach and tighten the metal tube fitting.
- Place the pipe from the clutch reservoir and tighten the clamp.
- Fill the reservoir with brake fluid, following the level marks.
The clutch master cylinder has been replaced.
Replacing the clutch slave cylinder VAZ 2107
Removal of the working cylinder should be done from the inspection hole or using a lift. The order of operations is as follows:
- Remove the return spring from the slave cylinder bracket.
- Unscrew the fitting of the tube coming from the master cylinder. To prevent brake fluid from leaking from it, you can put a cap on it, removed from the cylinder bleeder fitting, or direct it into a container prepared in advance.
- Unscrew the two bolts connecting the slave cylinder to the gearbox and remove them together with the plate.
- Remove the clutch slave cylinder.
This is interesting: Do-it-yourself repair of the VAZ 2114 mass air flow sensor
The new working cylinder is installed in the reverse order of removing the old one.
After replacing any of the cylinders, the hydraulic drive system must be pumped. The work must be carried out together with a partner. This is done like this:
- Place a hose on the fitting of the working cylinder and immerse its end in a prepared container for brake fluid.
- Depress the clutch.
- Unscrew the fitting on the working cylinder 1 turn.
- Wait until air bubbles stop coming out and tighten the fitting.
- Repeat the operation until air stops coming out of the fitting. At the same time, monitor the fluid level in the clutch reservoir.
- Tighten the fitting and put on the cap.
There are several ways to bleed the clutch on a VAZ 2107, here is a video about the most popular ones
Bleeding the clutch
After repairing or replacing the VAZ 2107 GCS, the clutch needs to be pumped. This will require an inspection hole or overpass.
Selecting and filling working fluid
ROSA DOT-3 or DOT-4 brake fluid is used as the working fluid in the VAZ 2107 hydraulic clutch drive.
The hydraulic clutch system of the VAZ 2107 is filled with ROSA DOT 4 brake fluid.
RJ is poured into the GCS tank, located in the engine compartment on the front bulkhead. To correctly fill the system, before filling, you need to loosen the air bleeder fitting on the working cylinder by one or two turns and tighten it after the liquid begins to flow out without gas bubbles. The tank must be filled to the appropriate level.
Bleeding the hydraulic clutch
It is advisable to use two people to bleed the hydraulic drive - one presses the clutch pedal, the other unscrews and tightens the air bleeder fitting on the working cylinder, having previously put a hose on it. You will need to do the following:
- Press the pedal firmly several times and hold it pressed.
- Unscrew the fitting and drain the liquid along with the air.
Continue the operation until all air has been removed from the clutch hydraulic drive.
VAZ 2107 clutch repair
Repairing clutch cylinders is somewhat more difficult than replacing them, but much cheaper.
Once the cylinders are removed, disassembly can begin. Let's start with the master cylinder:
- Use a thin screwdriver to remove the retaining ring.
- Remove the fitting and gasket.
- Remove the boot by prying it off with a screwdriver.
- Unscrew the cylinder plug using a 22mm wrench.
- Pull out the retaining ring and use a screwdriver to remove the inside of the cylinder.
To restore the master cylinder, the rubber seals must be replaced. It is also necessary to check the condition of the spring, the inner surface of the cylinder and the piston. If there are burrs or damage, parts must be replaced.
Before assembly, parts should be thoroughly cleaned and dried. It is unacceptable for gasoline or oil to get inside the cylinder - they destroy the rubber seals.
Assembly is carried out in the reverse order of disassembling the cylinder.
The clutch slave cylinder, despite some design features, is repaired in the same way as the main one.
After repairing the cylinders and installing them in place, it is necessary to bleed the hydraulic clutch drive.
Fault diagnosis
Identifying the causes of a clutch drive malfunction begins with an external inspection and check of the master and slave cylinders. The main cause of malfunctions of these components in most cases is wear of the rubber cuffs and wear on the walls of the mechanism. In this case, the main and working drives must be unconditionally replaced; attempts to repair them rarely give a positive result.
Master cylinder
So, we have removed the main cylinder and now we begin to disassemble it.
VAZ 2107 clutch master cylinder repair
- We start by removing the fitting. Use a screwdriver to remove the retaining ring.
- After which you can easily remove the fitting with the gasket.
- Now remove the rubber boot (protective cap) by simply prying it with a screwdriver or other convenient object.
- Now, using a 22 key on the other side, you need to unscrew the plug of the VAZ 2107 clutch master cylinder.
- You also need to remove the retaining ring from the boot side. This can be done using two screwdrivers, or special pliers. It is more convenient to use expansion pliers.
- Now you can easily remove all the insides of the cylinder.
Now about damaged parts and their replacement:
- All rubber seals should be replaced. 2 rubber rings - on the piston and pusher rod, one on the fitting, and we also replace the protective cap if necessary.
- If necessary, replace the spring. If it is deformed or damaged.
- Also pay attention to the internal mirror of the cylinder. It should not have burrs or chips.
- If the piston is damaged or the pusher is bent, then it is better to replace the cylinder with a new one.
- When assembling, all parts should be washed very thoroughly.
Note! Never wash parts in gasoline or oil and do not allow these liquids to get inside the cylinder. Lubrication is carried out only with brake fluid!
Then install the cylinder back on the car. This is how the clutch master cylinder is repaired on a VAZ 2107 car.
Replacing the clutch master cylinder on a VAZ-2104-2107
The main purpose of the clutch master cylinder is that it transmits force to the slave cylinder from the clutch pedal using working fluid.
If the master cylinder is faulty, vehicle control will be impaired and it will be impossible to disconnect the transmission from the engine.
How to determine if the clutch master cylinder is faulty:
- Periodically check the level of working fluid in the tank. A sharp decrease in it will indicate a system malfunction;
- check for leaks in the main and working cylinder housings;
- failure of the clutch pedal, which occurs due to the entry and accumulation of air in the clutch system;
- underpressure of the pedal and vibration of the gear shift lever.
Main types of faults:
- there is a leak in the master cylinder;
- cuff wear;
- piston wear;
- the inside of the case is damaged (chips, scratches, etc.);
- For all classics of the Auto VAZ family, the clutch device is the same, including for 2107. The sequence of actions is the same.
There are two ways to eliminate a malfunction of the master cylinder - replacement with a new one and repair. What can be repaired:
- replace rubber cuffs;
- frame.
These actions do not always lead to the desired effect, especially on an old car with decent mileage. It is recommended to replace the master cylinder with a new one. Its cost is not high, approximately from 450 to 500 rubles. It's better to buy the original.
What reasons will indicate a malfunction?
The following signs will help you understand that the clutch master cylinder is malfunctioning:
- a sharp decrease in the level of working fluid in the tank;
- traces of leaks in the area where the working and main cylinders are located;
- a kind of “failure” when pressing the clutch pedal;
- inability to fully press the clutch pedal.
Among the main types of malfunctions noted by experts, it is worth highlighting the following:
- malfunction of the cylinder itself;
- worn cuffs or piston;
- filling the system with low-quality brake fluid, which may contain both numerous dust particles and an excess of moisture.
To eliminate the causes of the malfunction of the main element, it is time to use two methods - replace the one that has become unusable with a new one or eliminate a minor breakdown by repairing it yourself. However, it is worth understanding that only rubber cuffs and the body can be repaired, and besides, repairing components will not always give the expected result. It should also be noted that as for the boot, it also needs to be inspected for the presence of large contaminations. According to experts, it is best to completely replace the cylinder, especially since its cost does not exceed 550 rubles.
Replacement
The cost of this type of work in a car service starts from 550 rubles. But for most car enthusiasts, this operation is not so difficult to perform on their own.
- new GVC;
- brake fluid;
- set of wrenches with extension;
- syringe or rubber bulb.
- Pump out the fluid from the hydraulic drive reservoir using a syringe or rubber bulb.
- Remove the expansion tank and move it to the side so that it does not interfere with work.
- Unscrew the tube with a 13mm wrench. Move it a little.
- Loosen the clamp and disconnect the rubber hose that goes from the tank to the cylinder.
- Unscrew the two nuts with a 13mm socket wrench and an extension.
- Remove the master cylinder from the studs.
- Replace the GCS with a new one.
- Reassemble everything in reverse order.
Bleeding the clutch
The replacement has been made, but you should not hit the road without bleeding the clutch system. The process is similar to bleeding the brakes and is carried out in the following sequence:
- Brake fluid is poured into the reservoir.
- A hose is put on the master cylinder fitting, the other end is lowered into a bottle filled with liquid. This will show how air leaves the system during the pumping process.
- The operation requires an assistant. One sits in the car and presses the clutch pedal 5-6 times on command, after which he leaves it pressed. The second one opens the fitting until the release of air stops. This is done several times until all air is removed from the clutch system.
- Tighten the fitting and add fluid to the reservoir.
Conclusion
After replacing the clutch master cylinder and bleeding the entire system, you can safely hit the road without fear that the clutch will fail and the car will lose control because of it.
Product location
The master cylinder on a VAZ 2107 is located under the hood, directly on the wall separating the interior from the hood, near the driver’s feet. Directly above it is the expansion tank, and next to it are the vacuum booster and the brake master cylinder. Usually, simply looking at the product is enough to determine the problem. The presence of a leak indicates that the part is faulty and requires repair or replacement.
Purpose of the device
Cars are equipped with clutch master and slave cylinders, without which the operation of the mechanism is impossible. The VAZ 2107 clutch master cylinder is designed to push out brake fluid. Below is a diagram from which you can visually find out the operating features of the unit.
When you press the clutch pedal, the piston moves in the device in question, thereby pushing out the brake fluid. This liquid enters the working cylinder through a tube, where the reverse process is observed (the liquid pushes out the piston). Brake fluid drives a piston, which is connected by a fork to the clutch disc. As a result, the clutch disc and flywheel are separated, allowing you to change gear. The GCS is also called the main one, since it is with its help that force is supplied from the pedal when it is pressed.
The need to replace the device: when required
Like all parts of any car, the GVC tends to wear out, resulting in the need for repair or replacement. The simplest breakdown of a product is wear of the boot, which can be determined by the characteristic signs of a fluid leak.
To identify a cylinder malfunction, an initial visual inspection is required. It is possible to repair a failed main circulation system on a VAZ 2107; for this you can look for repair kits, but this is not always rational due to the quality of modern spare parts, so it is easier and faster to replace it entirely. The malfunction can also be determined by the characteristic loss of pressure in the system, which is determined by pressing the pedal. Let’s take a closer look at how to change a faulty VAZ 2107 mechanism.
We change it ourselves
Replacing the VAZ 2107 clutch master cylinder begins with the need to pump out the brake fluid from the hydraulic reservoir. This can be done using a syringe or a rubber bulb. Together with this socket or a 10mm wrench, unscrew the bracket securing the expansion tank and move it to the side to gain access to the cylinder.
The next step involves removing the clutch expansion tank hose. To do this, you need to loosen the hose clamp, then disconnect the hose and position it so that it does not interfere with further work. If you want to remove the tank completely, this is done very simply.
Further actions are performed in the following sequence:
- Using a “10” wrench, you need to unscrew the pipeline securing nut to the device. Once the nut is unscrewed, the tube can be moved to the side.
- There is a hose nearby near the steel pipeline, which also needs to be disconnected from the main device. This can be done by loosening the fixing clamp.
- The GCS is fixed to the body using two fastening nuts. To unscrew them, you will need to use a wrench with an extension and a “13” socket. After unscrewing the two nuts, you can remove the product and drain the remaining brake fluid from it. If it is not possible to dismantle the unit, you can press the clutch pedal, as a result of which it will move.
- But repairs are usually not rational, so after removing the old one, a new unit is installed in its place. Installation is carried out in the reverse order of removal. After installation, it is necessary to carry out the process of pumping the hydraulic drive, first pouring fuel fluid into the tank. You can find out how the system is pumped from the relevant material on the website.
Dismantling the hydraulic drive
To perform the operation we will need:
- container for operating fluid and a large-volume syringe.
- set of wrenches and sockets;
- screwdriver and pliers.
The order of work is as follows:
- Brake fluid is pumped out from the expansion tank of the master cylinder of a VAZ 2107 car using a syringe. A rubber tube is disconnected from the drive, from which the remains are also poured into the prepared container. If liquid gets on paint surfaces, they must be wiped with a damp cloth.
- Using an open-end wrench set to “10”, unscrew the fitting of the pipeline connecting the main and working hydraulic drives.
- Using a “13” socket and an extension adapter, unscrew the nuts holding the assembly to the engine compartment panel.
- To remove the master cylinder from the studs, simply press the clutch pedal, this will move it out of place, after which you can pull it out by hand.
The work on removing the unit is completed, and you can begin installing the spare part.
Hydraulic drive installation
Replacing a mechanism involves purchasing it in a retail network or via the Internet. Installation work is performed in the following sequence:
- The clutch master cylinder of the VAZ 2107 is put on the studs and pushed all the way to the base.
- The nuts are screwed onto the fasteners and tightened with a wrench to “13”.
- The union nut of the pipeline laid to the working hydraulic drive is screwed into the main cylinder.
- The rubber tube is connected to a plastic connecting element and secured with a clamp.
- The expansion tank is filled with brake fluid, which enters the main and slave cylinders of the clutch through tubes. Replacing the fluid in the system is mandatory due to wear products.
This is interesting: Do-it-yourself trimmer carburetor adjustment
Upon completion of installation of parts, it is necessary to inspect and check the tightness of the nuts. Replacing the main or working clutch drive of a VAZ 2107 car ends with bleeding the system.
Clutch master cylinder VAZ 2107
The VAZ 2107 hydraulic clutch drive is the best option for rear-wheel drive vehicles. An important role in the hydraulic drive system is played by the clutch master cylinder (MCC).
Purpose of the GVC
The GCS converts the force of pressing the pedal into working fluid pressure (WF), which is transmitted through pipelines using the working cylinder piston (WCC) to the fork rod. As a result, the latter rotates on a hinged support and moves the pressure bearing, turning the clutch (MC) on or off. Thus, the GVC performs two functions:
- converts pressing the clutch pedal into fluid pressure;
- transmits pressure to the working cylinder.
Operating principle of the GCS
To create pressure in the hydraulic system you need:
- working environment;
- cylinder with piston;
- the force that causes the piston to move.
The VAZ 2107 MS drive uses brake fluid (ROSA DOT-4 is recommended), which practically does not compress and does not have a negative effect on rubber products.
The piston moves through a rod connected to the clutch pedal. The pressure in the system is created by analogy with a medical syringe due to the fact that the piston and the hole through which the gas is ejected have different diameters. The system differs from a syringe in that the GCS provides for the forced return of the piston to its original position. In addition, the heating of the fluid and moving parts during operation is taken into account.
The pedal moves the pusher, which, in turn, moves the piston and creates pressure in the hydraulic drive system
The GCS works as follows. Working fluid through hole 19 is supplied from the tank into the working cavity 22 in front of the piston. When you press pedal 15, pusher 16 moves and, resting against piston 7, moves it forward. When the piston closes holes 3 and 19, the pressure of the liquid in front of it will begin to increase sharply and will be transmitted through the pipelines to the RCS piston. The latter will turn the fork through the pusher, and its front ends will move the clutch with the release bearing (VP) forward. The bearing will press on the friction spring of the pressure plate, which, moving towards the VP, will release the driven disk, and the clutch will disengage.
When the pedal is released, the reverse process will begin. The pressure on the piston will disappear, and due to the return spring 23 it will begin to move to its original position. At the same time, the RCS piston and the fork return spring will also begin to move in the opposite direction and create pressure in front of it, which will be transmitted back to the RCS through the pipeline. As soon as it becomes greater than the force of the return spring of the GCS piston, it will stop. Through the bypass channel in piston 21, the inner surface of the floating sealing ring 20, which acts as a check valve, will be under pressure. The ring will flatten and block the bypass hole 3 in the cylinder body. As a result, a slight excess pressure will remain, which will remove all the play resulting from wear of the pushers, fork eyes and release bearing. As the temperature in the working chamber of the cylinder increases, all parts and working fluid will expand. The pressure in front of the piston will increase, and it will move back a little, opening compensation hole 3, through which excess liquid fluid will flow into the tank.
This explanation is necessary in order to understand how important it is to monitor the serviceability and cleanliness of the GVC. If the compensation hole in the piston or housing becomes clogged, the temperature inside the cylinder will quickly rise, which will create excess pressure in the master cylinder. It can squeeze out the gaskets and fluid will begin to leak. The pedal will become stiff and the O-rings will wear out faster.
Location of the GVC
Since the pusher must be positioned horizontally and fit exactly into its piston, the GCS is mounted on the front partition of the engine compartment on the left side. It is impossible to install it any other way - it is screwed onto two studs welded to the partition. No additional conditions are required to dismantle it. Access to the fastening nuts, pipeline fittings and reservoir hoses is provided by simply lifting the hood lid. At the same time, the main brake cylinder should not be confused with the main brake cylinder (MBC), which is located nearby, a little further from the sidewall of the left wing. The GTS is larger and more complex; more tubes fit into it.
Clutch mechanism design and purpose
What does the brake master cylinder repair kit consist of and how to change it?
The clutch mechanism is the thing that transmits torque through friction forces. As mentioned above, this ensures that the engine is disconnected from the box and switched back on smoothly.
Main elements of the clutch mechanism:
— driven disk with special wear-resistant linings;
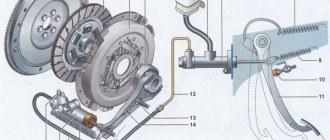
- drive disk - flywheel; — pressure plate with springs; - crankcase and casing. Now, using the VAZ 2101 (13) as an example, let’s look at the design of the mechanism and clutch drive. The Zhiguli has a single-plate, dry, permanently closed clutch, with a central pressure diaphragm spring and a torsional vibration damper on the driven disc.
Clutch assembly for Zhiguli VAZ 2101
1 – bleeder fitting; 2 – clutch pressure spring; 3 – pressure spring stepped rivet; 4 – pressure disk; 5 – driven disk; 6 – flywheel; 7 – clutch housing; 8 – bolt securing the clutch housing to the flywheel; 9 – gearbox input shaft; 10 – clutch release bearing clutch; 11 – clutch release fork; 12 – ball support for the clutch release fork; 13 – clutch release bearing; 14 – thrust flange of the pressure spring; 15 – clutch release fork cover; 16 – fork spring; 17 – support ring of the pressure spring; 18 – clutch casing; 19 – clutch release fork pusher; 20 – adjusting nut; 21 – lock nut; 22 – protective cap; 23 – clutch release cylinder (working cylinder); 24 – fork release spring; 25 – tension spring bracket.
Clutch pedal and master cylinder
1 – plug; 2 – main cylinder body; 3 – bypass (compensation) hole; 4 – fitting gasket; 5 – fitting; 6 – lock spring washer; 7 – piston of the main cylinder; 8 – sealing ring; 9 – pusher piston; 10 – hook; 11 – bracket for clutch and brake pedals; 12 – clutch pedal servo spring; 13 – clutch pedal release spring; 14 – clutch pedal travel limiter; 15 – clutch pedal; 16 – piston pusher; 17 – protective cap; 18 – retaining ring; 19 – inlet; 20 – sealing ring (ring valve); 21 – piston bypass hole; 22 – working cavity of the cylinder; 23 – spring; 24 – gasket.
Slave cylinder and clutch release fork
1 – clutch release bearing; 2 – ball joint; 3 – clutch release fork; 4 – pusher; 5 – adjusting nut; 6 – lock nut; 7 – tension spring; 8 – housing plug; 9 – fitting for bleeding; 10 – cylinder body; 11 – sealing ring; 12 – protective cap; 13 – piston; 14 – seal; 15 – plate; 16 – spring; 17 – support washer; 18 – retaining ring.
Main malfunctions of the clutch 1. Incomplete disengagement of the clutch (the clutch “drives”); 2. Incomplete engagement of the clutch (the clutch “slips”); 3. Jerks when the clutch operates; 4. Increased noise when disengaging and engaging the clutch.
Popularity: 11%
Selection of GVC for VAZ 2107
The best option for replacement is to purchase a GCS designed specifically for classic VAZ models. Clutch master cylinders from UAZ, GAZ and AZLK vehicles are not suitable. The same applies to foreign analogues - foreign cars with rear-wheel drive are equipped with GVCs, which only highly qualified specialists can adapt to the VAZ 2107 (different sizes, different threads for pipelines, different pipe configurations). However, you can easily replace the original cylinder with a GCS from a VAZ 2121 and from a Niva-Chevrolet.