Constant improvement of power plants has a positive effect on the overall performance of the engine, but not very much on the overall technical part of the car. After all, the simpler the mechanism, the higher its reliability.
For clarity, you can consider the fuel system of a gasoline engine. Previously, the carburetor was responsible for mixture formation and fuel dosage in an engine with such a system. The carburetor itself is almost completely mechanical. Only at the last stage of using the carburetor power system were idle solenoid valves used. This ensured high reliability; a malfunction in the carburetor could only result from severe contamination or violation of the adjustments. But these malfunctions were eliminated quickly and at virtually no cost.
But the carburetor could not provide accurate fuel dosage at different engine operating modes, which led to constant excessive fuel consumption.
Over time, the carburetor power system of a gasoline engine was replaced by an injection system. This system in its design implies the presence of an electronic system control unit. The presence of the block made it possible to accurately control the fuel dosage under different engine operating conditions. This has a positive effect on both fuel consumption and engine power, since so much fuel enters the combustion chamber to ensure maximum power output.
But the injection system is structurally more complex, and in order for the electronic control unit to perform its job correctly, the engine must be equipped with a large number of sensors that make certain measurements, on the basis of which the electronic unit performs its function. Among these sensors there is also a crankshaft position sensor, or in simple terms - a crankshaft sensor.
Crankshaft sensor. Why is it needed and how does it work
The crankshaft sensor on an injection engine is needed to determine the angular position of the crankshaft, as well as to determine the moment when the first and last piston pass the top dead center (TDC). This sensor transmits these indicators to the electronic unit, which determines the crankshaft speed and, based on this, makes corrections in the ignition system and fuel supply system.
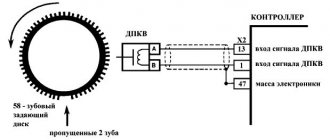
Most often, induction crankshaft sensors are used on cars. Its operation is based on a change in the magnetic field that the sensor creates when a metal object passes through it. On engines this is implemented like this: a special metal toothed synchro disk is installed on the crankshaft; it is usually installed on the generator drive pulley. There is a toothed rim around the circumference of this disk, but in one place two teeth in a row are missing. The crankshaft sensor is located opposite this disk at such a distance that the tops of the teeth fall into the magnetic field of the sensor. The crankshaft position signal is those two missing disc teeth. The part of the disk where there are no teeth passes through the magnetic field of the sensor, changing it. The sensor detects this change and transmits it to the control unit.
The engine control unit
To process readings from all sensors and control the engine, a special “brain”, an electronic engine control unit, is used. This part is used to take readings from sensors and, based on these readings, adjusts the fuel mixture, etc. A part rarely fails, but its main enemy is moisture; when water gets into the ECU, oxidation forms in it, which can cause short circuits and damage to the unit.
Signs of sensor malfunction
Since fuel dosing and the ignition system are adjusted based on the signals of this sensor, its malfunction leads to signal distortion and, as a result, interruptions in the functioning of the power plant or the inability to start.
Signs of a broken crankshaft sensor are:
- the engine does not start and the “Check engine” signal;
- difficulty starting the engine;
- instability of engine operation under different modes;
- a noticeable drop in engine power for no apparent reason;
- When the load increases, engine detonation appears.
If at least one of these malfunction indicators appears, you should find out whether the sensor is the cause of the engine malfunction. But to do this you need to know how to check the crankshaft sensor.
Coolant temperature sensor
To adjust the fuel mixture depending on the coolant temperature and to automatically turn on the cooling fan in the Lada Largus car, a coolant temperature sensor (DTOZH) is used. The sensor is located near the thermostat and has a thermoelement inside it, which changes its resistance depending on the coolant temperature.
Signs of malfunction:
- The car does not start well when cold or hot;
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Black smoke from the chimney;
Where is and how to check the crankshaft sensor
Before checking, you need to know where the crankshaft sensor is located in order to remove it from the car. Since the synchronization disk is located on the drive pulley, you need to look for it there. It is located not far from the disk, it is installed in its seat and secured with one or two bolts. Before removing, its wiring must be disconnected from the chip.
When dismantling, it is important to mark its position, so that later it can be correctly placed in its seat. First you need to give a visual assessment of the condition of the sensor. Its body should not be damaged. Over time, the core of this sensor can become covered with dirt, which can also affect the readings. Before checking, it must be thoroughly cleaned of dirt. To do this, you can use a rag soaked in alcohol or gasoline.
How to check DPKV with a multimeter
Set the multimeter to ohmmeter mode and connect the probes to the DPKV contacts. The resistance should be between 550-750 Ohms.
Set the multimeter to voltmeter mode (with a measurement limit of up to 200 mV). Connect the probes to the sensor contacts and bring a steel object to the sensor core several times. If the sensor is working properly, the device should detect voltage surges. You can more accurately check the DPKV without removing it from the engine. Rotate the crankshaft pulley and monitor the voltmeter readings. In a working DPKV, the voltage at the terminals reaches 0.3 V.
If the DPKV turns out to be serviceable, and the error (for example, p0335) in the engine control system has not disappeared, then you should clean the sensor of dirt and check the integrity of the wire and the quality of the connections in the circuit.
Let us remind you that the engine control system includes a number of other sensors that we talked about earlier.
Keywords: Lada Granta sensors | Lada Kalina sensors | Lada Priora sensors | Lada Vesta sensors | Lada Largus sensors | 4x4 sensors | lada xray sensors | ECM Lada Vesta | ECM Lada XRAY | ECM Lada Largus | ECM Lada Granta | ECM Lada Kalina | ECM Lada Priora | ECM 4x4 | Niva sensors | esud niva | universal article
0 0 0 0 0 0
Share on social networks:
Checking the crankshaft sensor
Checking the condition of the sensor can be superficial, in which only the resistance of its winding is measured, or deep, in which all basic parameters are checked. Let's consider both types of checks:
- For a superficial check, it is enough to have only an ohmmeter. Using this device, the winding resistance is measured. This indicator may differ on different cars, but usually it is 550-700 Ohms. If during measurement the resistance reading is greater or less, the sensor is faulty.
- An in-depth test is more complex and will require a megohmmeter and an inductance meter.
A megohmmeter measures the insulation resistance of the sensor when a voltage of 500 V is applied to it; at this voltage, the resistance should exceed 20 MOhm.
An inductance meter checks the inductance of the sensor. For a working sensor, this indicator should be at the level of 200-350 MHz.
Video: Crankshaft position sensor. Examination
These sensors have a non-separable design and cannot be repaired. Therefore, if the check shows that it is faulty, then it is simply replaced.
Knock sensor
In all engines, due to differences in fuel quality, detonations can occur that can damage the engine if they are not eliminated in time. To capture and eliminate detonations in the Largus engine, a knock sensor is used, which detects them and sends signals to the ECU, which changes the ignition timing to reduce vibrations in the engine. The sensor is installed on the cylinder block in the middle, near the oil dipstick.
Signs of malfunction:
Replacing the crankshaft sensor
So we know where the crankshaft sensor is because it was removed before. There is no such situation as with one of the sensors - a lambda probe, when it is possible to use a universal sensor, you just need to re-solder the wires under the chip, but with the crankshaft sensor there is no such situation. And all because the external parameters of this sensor may differ in different cars, so you will need to purchase this sensor only for a specific car model.
The seat must be thoroughly cleaned before installation. When installing a new crankshaft sensor, it is important to take into account such a parameter as the distance from the core to the rim of the synchro disk. This parameter can be found in technical. documentation for the car. Before installation, you need to measure this distance. To do this, you can use a caliper.
First you need to measure the distance from the edge of the sensor seat to the top of the synchro disk tooth. Then you need to measure the overhang of the core. To correctly adjust the distance, you can use washers of different thicknesses.
The marks made when removing the sensor will help you correctly install the sensor in place. In order, again, not to violate the distance, it is advisable to secure the new sensor using old fasteners. When tightening the bolts, do not apply strong force so as not to crush the sensor housing.
After installation, you will need to reset the on-board computer to get rid of the “Check engine” signal. Then you can check the performance of the power plant in different operating modes. If the problem persists, then you need to look for the cause further.
Phase sensor
Many modern cars are equipped with phased fuel injection, which reduces fuel consumption and increases engine efficiency. Phased injection allows for the implementation of a phase sensor (camshaft sensor). The DF reads readings from the rotation of the camshaft pulley and transmits the readings to the ECU. The sensor operates based on the Hall effect. Installed near the intake camshaft pulley.
Source
Removing the crankshaft position sensor Lada Largus
Tools:
- Driver for socket attachment
- Knob attachment 10 mm
We remove the crankshaft position sensor to check or replace, as well as when dismantling the gearbox.
We show the operations on a 1.6 (16V) engine; on a 1.6 (8V) engine we perform the work in the same way.
Removing the crankshaft position sensor
1. Remove the air path resonator. Disconnect the engine management system wiring harness connector from the coolant temperature sensor.
For clarity, we show the operation of dismantling the sensor with the heater radiator hoses removed.
2. Unfasten the plastic holder securing the wiring harness of the engine management system.
3. We move the wiring harness away from the crankshaft position sensor.
4. By pressing the lock of the engine control system wiring harness block, remove the block from the crankshaft position sensor connector.
5. Using a 10 mm socket, unscrew the two bolts securing the sensor and the wiring harness holder bracket.
6. Remove the sensor and the wiring harness holder bracket.
7. Install the crankshaft position sensor in reverse order. Tighten the sensor mounting bolts to the prescribed torque.