With the onset of cold weather, many car owners experience all the “delights” of the cold season - difficulties begin with starting the engine. The reasons may actually be both the battery and the starter. This problem, when the starter turns poorly when cold, is quite common, regardless of the make of the car. As for the battery, the battery may be old or dead. And many people remember such a concept as “lighting a car.” To understand what exactly is the cause of the identified problem, you need to understand where to “dig”, in what direction to move?
The battery is charged - the starter does not turn at all
In practice, there are much more often cases when the starter struggles or shows no signs of life at all due to a discharged battery. Here the repair is as simple as a door - charged the battery and started. However, it is not so uncommon for a situation where the battery is new, fully charged, but the starter still stalls or completely refuses to do its job. This is where you should start.
How to check the battery charge level
In order for a working starter to work reliably, the battery must be charged at least 30%. This is if it is new or purchased relatively recently. If the battery is already “tired”, then being charged and at 50-60%, providing the starter with the necessary current within a few seconds may be an impossible task for it.
How can you quickly and without a specialist check whether the battery is charged and by what percentage? There are only three ways to do this:
- Voltage measurement . This method is suitable only for those cases when the battery has not received a charge for at least 8, or even 12 hours. If you recently drove a car, just started the engine, recharged the battery from a charger, this method is useless. If the battery was at rest for the specified time, then by the voltage at its terminals you can easily determine its charge level. If the device (multimeter in voltmeter mode) shows 12.7 V, the battery is 100% charged. Voltage 12.6 V is already 90% and so on. Accordingly, if the voltmeter shows 12 V, or even less, then the battery is charged 30% or less.
- Electrolyte density measurement . The advantage of this method is that to assess the charge level of the battery, you do not need to “wait” for 8-12 hours, which is necessary to equalize the voltage. The charge determined by the density of the electrolyte will be correct, even if you take the measurement directly while charging the battery from a stationary charger. This method also has one significant drawback - not all modern batteries have liquid electrolyte or access to it. A 100% charged battery will have an electrolyte density of around 1.26-1.27 units. Indicators at the level of 1.1-1.2 indicate that the battery is almost “dead”. You can also focus on a clear percentage scale, which is probably found on any car hydrometer (a device for measuring electrolyte density).
- Load fork test . Not every car enthusiast has such a device. But if there is one, the instructions for it describe in detail and clearly how to check the condition of the battery using a load plug.
- So, the battery is sufficiently charged...
But the starter still doesn't turn over
In such a situation, there can be, offhand, three reasons:
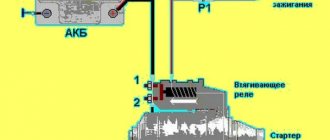
- Retractor mechanism jammed . This unit is part of the starter itself. With its help, the starter drive gear is brought into engagement with the engine flywheel. When the retractor jams, then when you try to start the engine, nothing happens at all - that is, no sounds are heard - clicking, rotation, and so on.
- Retractor mechanism failure . The node works, but does not work as it should. The retractor seems to be trying to bring the drive gear to the flywheel, over and over again. But the crankshaft does not rotate. This problem can be easily diagnosed, since if it occurs, characteristic clicking sounds or even a metallic ringing can be heard when trying to start the engine.
- Starter malfunction . When, when turning the ignition key, a clicking sound is heard once, after which nothing happens, the starter takes over or its main unit, which is a conventional electric motor, does not work. That is, the drive gear is brought into engagement with the flywheel (the same clattering sound), and this is where all the work ends. As a rule, at this moment there is a severe voltage drop in the on-board network, which can be seen by a flashing or dimming dashboard.
What to do if you experience one of the problems described is described below in the section on repairing and servicing the starter yourself.
Problems with the fuel system
Even the most “vigorous” battery and a new, working starter will not be able to start the car if problems arise with the supply of fuel to the cylinders. For this reason, the next thing to check is the engine power supply system.
1.Fuel pump
For carburetor and diesel engines, this unit is located directly next to the cylinder head or block. Injection power plants are equipped with an electric pump, which is installed in the fuel tank. Their operation is judged by a short buzzing sound that appears after the ignition is turned on. As for fuel pumps in carburetor engines, they are mechanically driven by a cam mounted on the camshaft.
It is easy to check the functionality of the fuel pump - to do this, remove the hose from the carburetor inlet fitting and lower it into a suitable container. After this, you should pump up the fuel using the manual pumping lever or by turning on the starter. If the result is negative, check the passage of gasoline through the fuel line and clean the mesh located in the top cover of the pump. If this does not help, then inspect the membrane and valves of the fuel pump. After replacing damaged and worn parts, the functionality of the device will be restored.
2.Fuel filters
Along the path of fuel passing from the tank to the engine there are several filter units - coarse meshes located on the fuel receiver, in the fuel pump and carburetor, and in addition, paper filters located in the section of the fuel line. The intensity and even the possibility of supplying fuel to the internal combustion engine depends on their purity. If you find a blockage, clean or replace the filter elements.
Throttle and injectors
Gasoline internal combustion engines operate on a fuel mixture, which is prepared in the carburetor or in the intake manifold (for fuel-injected cars). In the first case, the fuel passes through a whole system of channels, jets and nozzles that are located in the carburetor. In the second, it is supplied by injectors according to signals received from the electronic engine control unit (ECU).
The air supply is metered using a throttle valve, which, depending on the engine design, can be mechanically or electrically driven. Clean the parts of this assembly and the throttle itself. Also check if fuel is being supplied to the cylinders. If you are dealing with an injection car, then press the fitting spool located at the bottom of the fuel rail - gasoline should flow out from there under pressure. If the stream is too weak, then check the filters, fuel line and pressure reducing valve of the fuel pump.
In carburetor engines, the fuel supply can be judged by sharply opening the throttle - in this case, a portion of fuel will be injected from the accelerator pump nozzle into the diffuser. In addition, for gasoline power units, inspect the spark plugs - they should not be dry. Otherwise, check for the presence of a control signal at the injectors. If everything is in order with this, then you should unscrew the ramp fastening and move it away from the manifold in order to inspect the spray nozzles when starting the engine. The absence of fuel streams or their weak intensity indicates the need to clean or replace the injectors.
As for diesel engines, fuel is supplied to them under high pressure, and a much more complex pump (fuel injection pump) and specially designed injectors are responsible for this. To repair these components, special equipment is required, so in this case it is better to contact specialists.
Something else useful for you:
Video: The starter hums, but the engine does not turn over
To check the ignition system, unscrew and remove the spark plug from one engine cylinder. Having installed the tip of the high-voltage wire on its contact nut, touch the spark plug skirt to the cylinder head and crank the engine with the starter. In this case, a powerful spark of a purple or blue hue should appear on the contacts. If the spark is too weak (or there is none at all), then we check the operation of the computer, ignition coils and distributor (for an old-style internal combustion engine).
The battery is charged - the starter turns barely
In fact, it is quite rare that the starter does not turn at all with a normally charged battery. More often than not, it happens that he strains, makes the sounds of a dying toad, and dies without starting the engine. And the battery, with all this, feels acceptable. With such symptoms, the cause should be sought among the following five options:
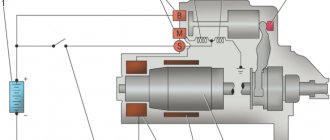
- Wear of starter parts . Most often, brushes or bushings are to blame in such cases (we’ll return to them later).
- Starter clogged . In quite rare cases, water or even dirt gets inside the unit in question. All this can both complicate the operation of the electric motor and even block it altogether.
- Long downtime . If you don’t touch the car even for several days, the oil that has settled on the engine parts during operation drains and flows into the crankcase. As a result, the rubbing surfaces remain completely without lubrication; accordingly, even the most energetic tandem of battery and starter may find it difficult to turn the whole thing over. This symptom is quite normal and goes away immediately after the first successful start of the engine.
- "Tight" gearbox . Solidified or frozen transmission oil, severe wear, minor breakdowns, etc., seem to “hold” the engine crankshaft connected to the clutch. As a result, it is difficult for the starter to “carry” two units at once. The problem goes away, if not completely, then at least partially, if you depress the clutch when starting the engine.
- "Tight" engine . At first, after a major overhaul, when the new parts have not yet gotten used to each other properly, cranking the engine (especially a cold one) requires a truly titanic effort. Therefore, it is quite natural that even a vigorous starter, powered by a fully charged battery, finds it as difficult to rotate the crankshaft as it is for a cyclist going up a hill to pedal. Similar problems can arise with a technically faulty engine - something gets stuck somewhere, gets caught, and so on.
Elimination of the first two reasons is described below, and the solution to the rest is already obvious.
High voltage part of the system
If the VAZ-2107 starts poorly or does not work at all, you need to check the center wire. It connects the distributor to the coil. To do this, the tip of the wire is carefully removed from the cover. Next, it is brought closer to any part that is in close contact with the mass of the machine. It does not matter whether this surface is painted or not.
Next, you need to secure the wire in such a way that there is a small space between the selected part and its tip (5-7 mm is enough). If the car has an electronic ignition, the conductor must be secured especially carefully. After all, if it falls on ground, all electronics will most likely fail.
You should also not scratch the central wire across the body. Do not hold the conductor with your hand. The electric shock will be quite strong. If there is a spark in this system, then the problem is in another system.
The engine is cold - the starter is “struggling”
Motorists usually encounter this kind of problem only in winter, with the onset of negative air temperatures. At the same time, the warmed-up engine is cranked by the starter cheerfully and vigorously. There are no problems in summer either.
In this situation, the reason should be sought in only two directions:
- Low battery . How to “calculate” it is described above. If this is the only problem, then it will go away immediately when the battery is recharged from a stationary charger or after the engine has been successfully started (from the generator).
- Thickened oil . When the temperature drops below the zero mark of the thermometer, any motor oil thickens - be it mineral water or synthetic. The viscosity class plays an important role, which is one of the main criteria for the selection and purchase of this consumable. If the engine oil is not selected correctly for specific climatic conditions, problems with the starter in cold conditions will continue until the end of winter.
If, however, the problem is not in the battery, then it is most likely in the oil. Apart from replacing it with an option suitable for the viscosity class, there is no other way to eliminate this reason (unless you always leave the car overnight in a heated garage, and never leave it in the cold for a long time).
Doesn't start well and boils
In this case, the reason lies in the coolant. Check its level. If necessary, dilute with distilled water. However, there is no need to mix different brands of antifreeze. It may foam, which will further accelerate overheating.
The thermostat may also break. The VAZ 2110 8-valve injector is equipped with a two-piston element. It's very easy to check. To do this, you need a burner and a pan of water. Place the thermostat in the container and wait for the water to boil. If bubbles appear and the piston does not move, it means the element is faulty. The temperature at which it should operate is indicated on the metal body of the thermostat. The element cannot be repaired - it must only be replaced. As a result, the system is unable to regulate the operating temperature of the antifreeze. The coolant moves only in a small circle. But the car may start poorly (every once in a while) due to an incorrectly adjusted ignition. Most "ten" cars have a distributor ignition. Here you need to set the correct lead angle.
The engine is hot - the starter turns sluggishly
If the starter turns the engine even when it has already warmed up to operating temperature, then you need to “dig” in the following directions:
- "Dead" battery . After several years of service or due to careless operation, the battery may not be restored even after starting the engine and generator. Or it is charging, but “gains” so few ampere-hours that there are simply not enough of them for the next job of the most powerful consumer in the car - the starter. The same applies to the strength of the starting current, which, unfortunately, decreases irrevocably in batteries over the years.
- "Tight" motor . This and the next two reasons are described above.
- Starter wear.
- Starter clogged.
- Starter malfunction.
- Poor electrical contact . Since the starter of an average production passenger car consumes 100-200 amperes of current during operation, wires of sufficient cross-section (almost as thick as a little finger) are needed to transmit it from the battery. If there is poor contact at the terminals, the power wires were incorrectly selected during repairs, broke, lost several wires, and so on, a noticeable voltage drop will occur in this area. Accordingly, the starter “will not receive” all the energy that the battery gives it, since a lot of it will be spent along the way (it will turn into useless and even dangerous thermal energy).
Whatever the cause of a stalled starter, it is fairly easy to diagnose. At the very least, most of the problems described can be identified and eliminated without any experience, simply by carefully (perhaps several times) reading this material.
battery
If the car engine does not start when you turn the key, the first thing to check is the battery charge level. The electric starter requires high current and can drain the battery after a few unsuccessful starts. If the car battery is discharged below 10.8V, the power supplied to the brushes is not enough to turn the small gear on the large flywheel. Especially during a cold start.
Two more common problems associated with the battery: an error in the on-board system (if the brain does not have enough current, the battery will not allow the engine to start), as well as oxidized or loose terminals. Wipe the battery terminals from oxide, reconnect the wires, checking the tightness.
Oxidized battery terminal