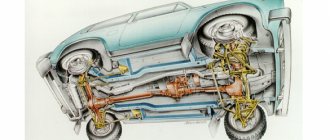
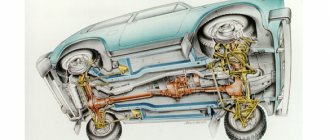
The Chevrolet Niva is one of the few Russian-made SUVs that, in addition to excellent cross-country ability, can also boast a relatively modern design. Therefore, it still enjoys well-deserved popularity in the market.
The Chevrolet Niva owes its good off-road characteristics to its predecessors - the VAZ2121, namely permanent all-wheel drive, with the possibility of forced differential locking. But before setting up the transfer case and using the gearshift levers correctly, you must first understand how this mechanism works and what happens during its operation.
The transmission of this type of car consists of several main components: cardan, gearbox, transfer case and axles. The main component in the bridge structure is the differential. If it were not there, the wheels would rotate at the same speed, which would lead to wheel slipping and excessive load on the axle. The presence of a differential allows you to avoid destruction of the axle due to the fact that when turning, torque is transmitted to one of the wheels.
The design itself provides for the transmission of torque to the wheel, which experiences less traction with the surface. Therefore, for example, a wheel that stands on ice or sand will spin faster than one that stands on asphalt.
The Niva design provides for the presence of three differentials. This is due to the presence of permanent all-wheel drive in the car. If the same force were transmitted to all wheels, then the car could only move in a straight line. But when turning, the forces between the wheels are distributed unevenly. Accordingly, two bridges connected to each other will invariably experience increased loads that can destroy the structure. There are some SUV models that do not have a center differential installed, but they use other technical solutions, such as clutches or all-wheel drive is not permanent.
What is forced differential locking?
It is only necessary in cases where, for example, only one of the 4 wheels will rotate. For example, when hanging horizontally, one wheel will be raised and maximum torque will be transmitted to it. In this case, all-wheel drive will be automatically disabled. Therefore, a forced differential lock is installed on the Niva. But it should only be used in off-road conditions. You can turn it on by moving the small lever forward.
The changes introduced by the American concern GM to the transfer case turned out to be quite minor. But at the same time they radically changed its structure. Compared to the old Niva, the need for an additional lever has disappeared and there are only two of them left. The modified location of the transfer case supports made it possible to reduce the vibration load on the body, thereby significantly reducing the noise level from the transmission.
Dealers and service centers
50 partner stores and 7 services in Russia
7. Distribution of torques in the transfer case
The question comes up quite often. Misunderstanding arises due to the fact that completely different physical phenomena are confused: force (moment) and motion (rotation).
First, a few starting points.
1. An unlocked symmetrical differential distributes the torque coming from the input shaft to the output shafts exactly equally: 50/50. This follows from the fact that the gear ratios from the input shaft to the output shaft are the same. In this case, the output shafts can rotate at different speeds, but the average speed (half the sum of the speeds) is equal to the speed of the input shaft divided by the gear ratio.
2. A locked differential ceases to be a differential. The movement (rotation) of the input shaft is transmitted equally to the output shafts. The speeds of the output shafts are equal to each other, and their sum is equal to the speed of the input shaft divided by the gear ratio.
3. If the total torque applied to the shaft (wheel) is not zero, the rotation will be accelerated or decelerated. This is Newton's second law. If the shaft or wheel rotates uniformly, the total torque acting on it is exactly zero. The absence of movement is also uniform rotation, but with zero speed.
There are three symmetrical differentials in the field. When they are all unlocked, each wheel receives 25% of the torque transmitted through the transmission from the engine. And the rotation generated by the engine is also transmitted to all four wheels, but not necessarily equally. For example, when turning, the rear wheels travel a shorter distance (smaller radius) than the front wheels, but all four wheels pull equally.
Let's consider a situation where one wheel is slipping, the rest are standing. All engine rotation is transmitted to the slipping wheel. Strange as it may seem at first glance, the slipping wheel accounts for 25% of the torque, exactly the same as the rest. But this moment is small: it is equal to the moment of friction (only in the transmission, if the wheel is completely suspended). This means that the moment on the other wheels is also very small, it cannot move the car. The car is stationary, and the suspended wheel rotates at a speed that is four times higher than it would be during normal movement at speed at the same engine speed and with the same gears in the gearbox and transfer case.
Differential lock
Forced blocking not only complicates the design but also automatically makes it more expensive and less reliable. But if you install a differential lock yourself, this is usually caused by the desire to replace the standard differentials with a forced locking mechanism. This can negatively affect the operation of the transfer case, so it is necessary to select those parts that will be compatible specifically with the Chevrolet Niva.
At the moment, among the solutions presented on the market, the most popular are those made on the basis of:
- pneumatics
- electronic control
- self-locking
Each of them has both advantages and some disadvantages in operation.
Varieties
There are two main groups of self-locking differentials. The first type works depending on the angular speed parameters along the axes of the vehicle. In turn, these modifications are divided into several subtypes, namely:
- disk versions;
- models equipped with a viscous coupling;
- options with electronic action.
The second type includes mechanisms that are locked in accordance with the torsional moments on the axes. This group includes worm modifications.
Self-locking system
Can be configured to the required switching threshold. This can be either a slight slip or uneven distribution of torque among the wheels. Such a connection is not rigid, and therefore does not place unnecessary load on the interaxial connection.
When installing a forced locking system on a Chevrolet Niva, you should remember that a constantly turned on system can put unnecessary stress on the transmission, so you should turn it on only when overcoming difficult sections of the road.
When to use and how to disable blocking
It is preferable to enable forced blocking in various modifications of the Niva in the following situations:
- The blocking must be turned on in advance if you have to overcome a difficult route.
- On sharp climbs uphill or when driving downhill.
- While crossing terrain with a top layer of sand.
- When you have to drive on snow drifts or an icy road.
Also interesting: Buy Niva Leather Steering Wheel Cover online, Niva Leather Steering Wheel Cover at a discount on AliExpress
Wheel locking is not necessary when driving quietly on a flat road within the city. Grip on asphalt surfaces will be decent, and traction will be distributed evenly by default.
Why do you need a self-block for Niva?
The presence of all-wheel drive in a car does not always give it the status of an all-terrain vehicle. Sometimes, due to the nature of their design, vehicles designed for off-road driving can become trapped on washed out roads. A self-locking differential is an important component of the car if the driver plans to use his Niva to drive on bad roads.
What is a self-block, or limited slip differential? This is a device that ensures wheel locking, and automatically, at the right time. It is an intermediate option between a full lock and a free differential. The self-block combines the capabilities of both of these devices.
Advantages and disadvantages
To find out which is the best self-locking differential for the Niva, you need to compare the advantages and disadvantages in relation to the standard analogue of the car. The benefits include:
- Increasing the vehicle's maneuverability on steep, sliding and bumpy surfaces.
- There is no need to make changes to the design of the machine, since the self-block is mounted in place of the standard element. It is recommended to carry out installation work in a specialized workshop or do it yourself.
- The mechanism in question operates automatically and does not require special training for the driver.
Disadvantages of installing a self-locking differential on a Niva:
- steering becomes tighter, which requires additional effort;
- the working life is less than that of the factory element;
- driving style changes when cornering;
- there is no complete guarantee of blocking.
Various modifications of self-blocks have their own nuances, depending on the manufacturer, type of development, and installed components.
Types of mechanisms
There are two main types of self-locking differentials, which include several more subtypes. The first type is devices that lock depending on the angular velocities on the vehicle axles. They can be:
- disk;
- with viscous coupling;
- with electronic locking.
The second type is mechanisms that lock depending on the torques on the axes. These include worm differentials.
There are also center and cross-axle differentials. They involve the distribution of torque between the axles and wheels, respectively. Depending on the moment of distribution attributable to the axles or wheels, symmetrical and asymmetrical types of mechanisms are distinguished. On vehicles called all-wheel drive, three types of differentials are installed at once: two of them are interwheel, and one is interaxle.
On the Niva it is possible to install electronic, mechanical (it is a conventional mechanism combined with a viscous coupling), and pneumatic differentials.
The electronic self-block has a very big advantage. To use it, just press a button. It works in automatic mode, but only when the car is traveling at a certain speed, which is below a threshold value. The system turns off when the speed exceeds the set speed.
The pneumatic differential is a mechanism mounted on two axles. The advantage is compactness. In its work it uses pneumatic systems.
The mechanical self-block is the simplest in its design; it is cheaper than pneumatic and electronic devices. The mechanism consists of two semi-axial and two spacer couplings, pins and springs. Quite a reliable design, despite its simplicity.
Functional purpose of the device
A rigid blocking is used on the Niva to balance the incoming load. The process is based on the unevenness of the path traveled by each wheel. The sides located closest to the center travel several times shorter than the wheels located on the outer side. At low travel speeds, some of the rubber wears out faster, and at high speeds, skidding occurs.
Electronic differential locking helps to avoid the above. In good condition, it transmits torque from 1 source to 2 different consumers. In order to understand how the mechanism works, it is necessary to imagine the following: from 1 source, each consumer receives a torque of different physical parameters. If the differential lock is set correctly, the difference in the amount of torque received ensures safe rotation of the wheels along the inner and outer radius. Physical wear or mechanical damage increases the likelihood of a skid accident
When operating a VAZ 2121 on roads with unsatisfactory surface quality, the importance of the differential increases
All-wheel drive vehicles, whose axles are coordinated by a differential, distribute torque evenly to all wheels. In case of slipping, the system automatically transfers maximum torque to them. The switching process does not take much time. In the event of a malfunction, 2 wheels slip, while the other 2 remain stationary. Differential locking helps to avoid this.
It forcibly distributes torque evenly over the front axle, between it and the axles. In case of temporary slipping, the device will provide the necessary uniform force to increase the quality of traction.
Characteristics and selection rules
The choice of a self-locking differential is determined by the car model, its operating conditions, driving style and many other parameters. For example, a ball differential increases steering load, which actually changes the driving style of whoever is behind the wheel. This is mainly felt when making U-turns and turns, but can lead to breakdowns of transmission components.
If you approach the choice of a self-block correctly, then you need to take into account which axle of the car the mechanism will be installed on, since the number of splines for different models is different - twenty-two or twenty-four.
The marking on the device packaging will tell you whether it can be used for a given car brand. The blocking coefficient also varies: for example, 0.5 or 0.7. These numbers show the amount of torque transmitted. What to choose is up to the driver.
Why is downshift needed?
By fixing the lever at the front, the gear ratio can be increased to 2.1. The lever in neutral indicates gear ratio 0.
Sources
- https://LadaAutos.ru/niva-2/kak-rabotaet-blokirovka-differenciala-na-nive-i-ee-sxema.html
- https://fb.ru/article/238437/blokirovka-differentsialov-na-nive-elektricheskaya-pnevmaticheskaya-mehanicheskaya
- https://auto.today/bok/1284-samoblokiruyuschiysya-differencial-na-nivu-prokachivaem-prohodimost.html
- https://www.izh-techno.ru/series/prinuditelnaya-blokirovka-niva
- https://fb.ru/article/240983/prinuditelnaya-blokirovka-na-nivu
- https://ProCrossover.ru/rossijjskie-krossovery/blokirovka-na-nivu.html
- https://expertVAZ.ru/niva/samoblokiruyushhijsya-different-na-nivu.html
Pros and cons of installing a differential on Niva
If you compare the self-block and the standard Niva differential, you can identify the negative and positive aspects of replacing the latter. First, about the advantages:
- Increases the vehicle's cross-country ability, making it suitable for driving on steep, slippery and uneven sections of the road.
- It is mounted instead of the original differential and does not change the design of the car. It is better to carry out the installation at a car service center, but it is quite easy to do it yourself.
- The full differential operates automatically during the driving process, without requiring additional actions or any driver training.
My review of Dak and Racing
It just so happened that I had to use the two mentioned types of self-blocks. Their price at the time of purchase was almost the same - ten thousand, the installation is also the same, but the result is completely different.
If the DAK failed after about six months, and not in intensive use, but when driving on ordinary forest roads, then the Togliatti one (val racing) is still working.
Maybe I was just unlucky, but I have repeatedly come across reports that there are problems with the quality of the metal in the production of DAKs. So think for yourself.
Is it necessary?
There are a huge number of opinions about whether a self-block is needed at all, and the most polar ones - from “why is it needed” to “is absolutely necessary.” As always, the choice is a personal matter and everyone must make it themselves.
It seems to me that everything depends on how and where you move in your car. If you go to the country or mostly on asphalt, then you definitely don’t need a self-block.
The situation is approximately the same if your hobby is off-roading and you are engaged in conquering impassable roads. Here, such “half measures” as self-locking will not work and here you need a full manual differential lock.
However, if your task is to overcome not too severe off-road conditions, driving along a wet, broken forest road, i.e. normal conditions without extreme conditions, then self-block can be a good helper in such conditions.
Maybe it seems to me, maybe I have the self-locking set up this way, maybe that’s not the issue, but often when the car starts to “slip”, a jerk in the opposite direction suddenly appears. It’s as if the car first went to where the wheel was blocked, and then it gained momentum again, and the car jerks in the opposite direction.
A self-locking differential for the Niva is a good addition that, if used correctly, can significantly improve its off-road properties.
DIY self-block installation instructions
To install a self-locking differential on a Niva, it is not necessary to contact a car service center. It is quite possible to do this with your own hands, provided that the person has a good understanding of the structure of the car. The type of differential and its installation location are not particularly important.
First you need to decide on the place where the work will be done; it should be spacious enough. Using several jacks, you will need to lift the Niva, dismantle the wheels, then drain the engine oil from the gearbox housing into some container and remove the drive axle drive. To do this, just use a spanner to unscrew all the nuts securing the front cover to the gearbox housing, remove the cover and gasket.
Now it is necessary to reliably and efficiently carry out the operation of dismantling the axle shafts, which is very difficult to do without a special puller. The metal is clamped on rotary slots, which requires a lot of effort, which not every person has enough. Dismantling the axle shafts is carried out as follows:
- Unscrew all the bolt nuts on the axle bearing mounting plate.
- The brake mechanism is fixed. This can be done using bolts or wire. If the mechanism is not secured, the brake lines may come off.
- The axle shaft itself is removed. With sufficient skill, this can be done by hand, but it is better with the help of a puller.
Then you need to change the bearings. This will require a hydraulic press. It will help ensure that the holder fits onto the shaft, and with fairly high accuracy. To replace you need:
- Unscrew the hub bearing nut and remove the bushing. Unscrew the nut securing the lever to the steering knuckle.
- Remove the locking plate and unscrew the lever from the steering knuckle.
- Having disconnected all the fasteners, separate the knuckle and the hub with the brake disc. Remove the bearing by first holding the steering knuckle in a vice. During assembly, the bearing is put on using a press.
After the clearances in the main gear are adjusted using special washers of variable thickness, you can begin assembling the unit. Adjusting the gaps is quite difficult, and you will need special equipment, but to ensure accuracy you can use a steelyard. To work with it, wind one end of a 1 m long cord around the flange and secure the other end to the scales. By pulling the device in the winding, you will need to record the turning moment.
To ensure proper operation of the gearbox, the parts are usually sealed before the halves are assembled. In its absence, malfunctions may occur during operation, as well as failure of certain spare parts. After applying the sealant, you need to wait a while for it to harden. Then new oil should be poured into the gear housing. All sealing joints that were damaged during dismantling, as well as those that show signs of oil leakage, must be completely replaced with new ones. Now you can start assembling all the mechanisms in reverse order.
After completing all the replacement and installation of parts, you must check the operation of the devices that provide vehicle braking. Their malfunction may affect road safety.
The feasibility of such an action as differential locking on a Niva depends on why the driver needs it. If you need to move through difficult areas, you will need it. If a car enthusiast intends to drive on a normal asphalt road, then installing a self-locking differential on the Niva is hardly worth it. Which self-block to choose and where to place it depends on the driver’s preferences.
If desired, you can lock the differential with your own hands in the drive axle gearbox of any car. A driver who uses his car exclusively on paved roads will most likely never have the desire to lock the differential. Another thing is for those who like to conquer off-road terrain.
Removing axle shafts and bearings
To install a self-locking differential on a Niva 4x4, you need to carefully and efficiently remove the axle shafts. A special puller will be required. Otherwise, this is problematic, since the metal sticks to the slots. Stages of dismantling axle shafts and bearings:
- Unscrew all the bolt nuts on the plate element for fixing the axle bearing.
- The brake block is secured with bolts or fittings of a suitable diameter. If you ignore this procedure, the brake lines will come off.
- The axle shaft is removed directly using a special device.
- To dismantle the bearings, you will need a hydraulic press, which will make it easier to fit the race onto the shaft with high precision.
- Unscrew the wheel bearing nut and remove the bushing.
- Unscrew the fastening nut securing the lever with the rotary cam.
- Remove the stupor plate and remove the lever.
- Disconnect all fasteners, disconnect the hub with the brake disc and the knuckle. Dismantle the bearing, having previously fixed the rotating element in a vice. The bearing is also installed by pressing.
How to do
The easiest way is to permanently lock the differential completely. But such a homemade blocking is acceptable for cars driving only off-road. For example, for rally-raid cars. To implement the idea, you need to remove the unit equipped with the differential and disassemble it. Then weld the satellites to the axles. Fixing the gears will allow the mechanism to divide the rotation speed between the axle shafts only in a ratio of 50 to 50. Making a limited slip differential with your own hands is a little more difficult than simply fixing the satellites. But such a modernization will not only improve the vehicle’s maneuverability in mud and snow, but will also not change the operation of the unit on hard surfaces. One version of such a device can be assembled from two brass or bronze bushings and a spring. Their sizes will depend on which vehicle transmission you are upgrading. Therefore, work begins with removing the assembly and disassembling the planetary gear. After this, you can take measurements, order the production of bushings and select a spring of suitable dimensions.
You will find out whether it is stiff enough after assembly by testing your homemade product. The spring is designed to press the pinion gears against the differential housing. Because of this, under the influence of friction, the satellites will rotate more slowly around their axis. The greater the friction force, the more evenly the speed of rotation of the driveshaft will be divided between the axle shafts. Metal bushings are needed to prevent contact of the satellites with the spring.
Of course, installing a factory-made differential lock is easier and the result of such an upgrade is better. However, it is expensive and practically eliminates creativity from the process. The cost of “self-blocks” for cars of the VAZ family is slightly less than 12 thousand rubles. But their installation requires only care and accuracy. There is no need for a special tool.
Which lock is better?
The answer to this question depends on what kind of car you have and where you drive it. Therefore, let’s say just a few words about the features of different types of blocking.
- Forced manual locking. The advantage is that it is completely turned on and off at the right time and, as a result, better cross-country ability of the vehicle. The disadvantages include the need for advance switching on and mandatory switching off.
- Automatic blocking. Switching on and off without driver intervention is a definite advantage. Noticeable inertia is its obvious drawback.
Chevrolet Niva expedition › Logbook › * Self-locking differential in the bridge.
Friends, I want to share with you my short report on the operation of a self-locking differential. I would like to warn you right away that this is my personal opinion, which was formed after two years of using such devices.
We will talk about a screw differential lock. In pursuit of the cross-country ability of my former field, I began to build self-blocks into the bridges. After the sale of the Niva, the megadevices migrated to the Chevy, but were later dismantled. The devices are of course very interesting and really help to increase the vehicle’s cross-country ability. The truth is not as much as you might expect. Let's just say that self-locking locks help you get stuck further than a standard differential. Sometimes automatic locking even gets in the way, especially on the front axle. This usually happens in slush or snow, when you need to turn onto a slope. The car stubbornly rows along the trajectory that it likes best, which does not always coincide with the driver’s opinion. Another minus of self-blocks, even if only in the rear axle, is that in order for it to work as expected, frequent maintenance is necessary. In my experience of operating a Chevy in almost civilian mode, about once a quarter it is necessary to remove the lock to tighten the trigger moment. After half a year it doesn't hold up at all. This happens because the device is built on the basis of friction, and what rubs tends to wear off. If you do nothing after the preload weakens, then nothing bad and nothing good happens. The dissolved self-block begins to work like a regular differential, and simply becomes a “pill for the placebo effect.” It is also worth noting that with a fully working self-block, you need to very carefully gas on any heterogeneous surface, including snow and slurry. Especially on large wheels with pronounced tread. It is very easy to collapse the axle shaft in this situation.
To check the operation of a self-locking differential, it is enough to simulate diagonal hanging. Raise the axle under the axle/lever with a jack and try to move out of such a “trap”. If the self-block does not work (requires re-tensioning), then those wheels that are raised in the air will spin, completely simulating the operation of the most ordinary differential. But I did not suggest this to you, and if you follow this method of verification, you rely entirely on your own peril and risk.
For myself, I came to the conclusion that the best blocking is a forced one, which can be turned off; then it interferes or is simply not needed. And the self-locking differential is too “sporty” and requires a lot of attention to maintain. Therefore, after the last weakening of the preload, I decided that this was not suitable for me.
Thank you all for your attention
Removing and disassembling the gearbox
Replacing a VAZ 2110 bearing
Needless to say, before you start replacing the bearing, you should remove the box from the car and disassemble it.
Removing the car box
Replacing a bearing on a VAZ 2110
Started:
- We install the car on the inspection hole;
- we lift the hood of the car and fix it tightly with something so that it does not wobble;
- remove the battery terminals;
- drain the oil from the gearbox.
Note. It is easier to dismantle the gearbox from a VAZ 2110 with an assistant.
- we start by dismantling the crankcase protection (it is secured with bolts that should be unscrewed);
- the ground wire must be removed by unscrewing the bolt;
- we find the tip of the clutch cable, which disengages the clutch and loosen the tightening of the nuts;
- remove the cable end;
- remove the starter and traction relay from the car;
- Now you should loosen the clamp holding the gear shift rod;
- the cable is disconnected from the speedometer drive;
- the reverse light wire is disconnected;
- we separate the guy wires from the car's suspension arms.
Note. To be able to separate the stretch marks, you will first need to loosen the nut.
- we find how the tie rod ball joint is attached to the swing arm (this is a nut that should be unscrewed);
- Now you should press out the ball joint pin (a special puller is used for this);
- remove the ball joint by unscrewing two bolts;
Bolts securing the ball joint
We take a pry bar, with which we squeeze out the shank of one grenade of the front wheel drive from the gearbox (the CV joint should be moved to the side);
You need to insert something instead of the grenade shank. For example, it could be an old CV joint (see VAZ 2110 replacing a CV joint - how to do it) or another technological plug.
- repeat the same operation with the second grenade;
- it's time to unscrew the clutch housing shield;
- Now you need to start removing the crankcase itself, which is attached to the cylinder block.
Note. To secure the process of dismantling the box, it is necessary to place appropriate wooden blocks on the components of the wings, which are located near the supports of the front pillars. It is on them that the engine will be hung. Don't forget that the wooden beam should only rest on the wing flanges!
- we proceed to removing the engine, which needs to be attached to a beam by a special eye, using a long bolt with a hook for this;
- unscrew the nuts securing the engine to the gearbox;
- we move the box away from the engine, removing the input shaft from the clutch;
- remove the box.
Explanation of operating principle
Translated from Latin, differentia means “difference.” In a car, a differential is a mechanism that distributes torque to the car axles. It definitely exists in every car. A simple differential is called classic, open or free.
Let's imagine that the rear axle gearbox does not have a differential, but there is a single axle, like a tricycle.
Since there is no absolutely linear movement, and the driver's hands almost never lie motionless on the steering wheel, it is clear that the path of the drive wheels will be very similar, but slightly different.
If there were no differential, then the path of the left and right wheels would be the same. Then constant slipping will become inevitable, since a common trajectory is “imposed” on the wheels. This results in increased tire wear and rapid failure of transmission units.
The task of the gearbox is to give the wheels independence and “freedom”, to separate their rigid connection.
How does a classic differential work?
If there is one drive axle (all VAZ classics), then one gearbox is required between the rear wheels, i.e. interwheel. In the case of a full-fledged jeep, there are as many as three differentials - two inter-wheel differentials for each axle, and an additional inter-axle one.
This mechanism (also called a gearbox) is installed in the rear axle housing. The drive gear transmits torque to the driven gear. It is distributed into two gears of the axle shafts, and they rotate the wheels.
Additional gears - satellites are a symmetrical equal-arm lever, and transmit forces equally to the wheels.
When the car moves in a straight line, the satellites do not rotate. As soon as the car slides onto uneven ground or enters a turn, that is, when each wheel has its own path, the satellites begin to rotate and redistribute the torque between the wheels of the drive axle, and to the axle shaft that has less resistance and is easier to spin.
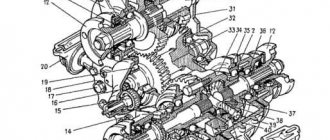
The VAZ differential is shown in the figure below:
8 — axle gear; 9 — satellite; 11 — driven gear of the main gear; 18 — drive gear of the main gear;
This is how the satellites behave and distribute the moment of movement in different areas:
- linear movement
- left turn
— the right wheel is slipping
From the analysis of the rotational speeds of the axle shafts and gearbox it follows that:
- If one wheel is stationary, then the free wheel rotates “for two”, and the rotation speed is doubled.
- If one wheel slips, it spins faster and starts to slip, and the second wheel with good grip will receive the same torque, since it is distributed equally, and the differential cannot give it all the traction.
- If the traction of a single wheel becomes less than the resistance to movement, the car will stop.
- In this case, the situation of point 1 arises, the running wheel stops, and the previously slipping wheel sharply increases speed.
- When you try to “add gas,” the speed of the slipping wheel increases.
So, a conventional gearbox does not help the drive axle on slippery roads and on surfaces with high rolling resistance (snow, sand and mud). The cost of a conventional gearbox is about 5,000 rubles.