Crankshaft sensor for VAZ 2115
VAZ 2115 (Lada Samara) belongs to small class passenger cars, produced by the Volzhsky plant until 2012. The model had a single body type - a sedan and was equipped with a line of productive 8-valve engines with an injector fuel supply system. The crankshaft sensor of the VAZ 2115 is not a frequent consumable of the model, but given that the last “Fifteen” rolled off the production line 8 years ago, drivers are increasingly noticing signs of an internal combustion engine malfunction, which are typical for a breakdown of the DPKV.
Purpose of dpkv
The crankshaft sensor on the VAZ 2115 belongs to the engine electrical control system. Based on the controller readings, the ECU arranges the ignition and the order of supply of the fuel mixture. DPKV, the second name of the element is a position sensor, monitors and transmits to the ECU the location of the crankshaft at any time. By processing information about the angular velocity and the frequency of its rotation, the ECU determines the moment of passing dead spots in the cylinders and calculates the operating mode of the following systems:
- ignition supply for each cylinder;
- injector opening time;
- gas distribution correction;
- control of adjacent systems of the output path, muffler, etc.
Crankshaft sensor 2115, an important component for the correct operation of the internal combustion engine, a faulty element leads to serious engine damage. Since the Lada Sputnik is equipped with injection engines, the part generates a signal to supply the ignition and to open/close the injectors; for carburetor engines, the unit only regulates the ignition operation. The sensor is located directly next to the crankshaft master or synchronization disk; the controller is mounted on a bracket screwed to the oil pump cover.
Reasons for failure of the DPKV
If a malfunction occurs, it is recommended to replace the crankshaft sensor with a new one.
Its cost is not so high - from 200 to 400 rubles, depending on the manufacturer and region. In addition, it is best to change the DPKV yourself, since a trip to a car service center is comparable in price to the cost of several sensors, while the procedure itself, as mentioned above, is quite simple. We can name several of the most common reasons why the DPKV fails. Most often, a banal mechanical deformation of the body occurs. It is made of plastic, so this problem may occur most often. In addition, the sensor fails as a result of a short circuit that occurs between the turns of the winding. As a result, the generation frequency transmitted to the ECU changes. Most often, this type of breakdown occurs in frequency-type sensors. Well, another fairly common problem is breakage of pulley teeth or wear.
Source
Construction types
The VAZ 2115 is equipped with two types of crankshaft sensors, which differ in design, but have the same principle of transmitting the read signal. The operation of any controller is based on two components:
- sensing element;
- toothed disc (synchro disc).
The master or synchro disk is installed on the crankshaft and has the same rotation speed with it. The disc rim is divided by 58 teeth, the empty space of two teeth is occupied by the synchronization point. The tracking element is located at a certain distance from the transverse axis of the disk, captures the moment of tooth transition and transmits the number of crankshaft revolutions to the computer.
According to the type of design, the sensors on the VAZ 2115 can be of the inductive type and based on the Hall effect. Optical sensors that use a light beam are rarely installed on cars, since the engine compartment is often highly dusty. There is a danger that the sensitive element of the light catcher will be clogged with grease, oil, etc.
The magnetic controller for VAZ is based on a core with a winding installed in a plastic case. The principle of signal transmission is based on the law of electromagnetic induction. On the winding of the core, when a part of the disk without a tooth passes next to it, there is no current; when a part of the disk with a tooth approaches, a magnetic field arises, the winding is excited, current induction appears, and a stable electrical signal is formed, which is transmitted to the ECU.
The advantages of the magnetic sensor are obvious: its operation does not require power from the on-board network. Accordingly, the risk of breakdowns is reduced; during diagnostics, only the condition of the winding, core and signal quality to the ECU are checked.
DPKV, the operating principle of which is based on the Hall effect, requires connection to the on-board network. The operation is based on the occurrence of voltage on two plates through which current passes.
The cost of controllers for the entire VAZ line starts from 200 rubles, so parts are not repaired, only replaced.
Kinds
Depending on the design and operating principle, there are three main types of crankshaft sensors. Let's look at the features of each of them in the table.
| Sensor type | Design Feature | How does it work |
| Inductive | Inside it is a metal rod with a magnet at the outer end. It magnetizes the rod. There is a copper winding around the rod, and its ends are connectors for connecting wiring | When a steel object is near the rod, signals appear on the terminals |
| With Hall sensor | The internal design of this type of sensor includes a Hall sensor | When a metal object approaches it, the state changes from zero to one and vice versa |
| Frequency | The design is based on reading pulse frequencies that are generated by the ECU | Pulses of a certain frequency are supplied to the sensor. When you bring a metal object, the generation frequency changes. By changing frequencies, the DC determines the presence of objects near it. The reaction occurs due to the metal teeth of the crankshaft crown |
Examination
Checking the DPKP is mandatory if the following symptoms are observed during the operation of the DVM.
- After parking, the engine cannot be started. There is no signal to the ECU, the unit cannot generate a signal order for the ignition to operate.
- While driving, engine thrust is reduced and dips in speed are observed.
- The "Check" warning light on the dashboard lights up.
- When shifting to a higher gear, detonation appears.
Before checking the crankshaft sensor, check the quality of the supply wire, if the car has a Hall element, and the signal transmission cable. In 90% of variants for VAZ, magnetic controllers are used; before checking, the part is dismantled, the connector plug is removed, and 1 screw is unscrewed from the bracket.
The sensor is checked with a multimeter, the tester is switched to ohmmeter mode and the inductor is checked for resistance.
Checking dpkv with an ohmmeter
Diagnostics is carried out after dismantling the part; on the VAZ 2115 it is difficult to get to the sensor, the part closes the air pipe. To quickly remove the element, use a 10mm socket, a ratchet and an amplifier. To check, use a multimeter, switch the device to resistance measurement mode and set the operating range, the upper limit is 2 kOhm.
Replacing the sensor
There are dozens of manufacturers on the market that produce original replicas of VAZ spare parts. Experts recommend choosing a universal controller from the MASTER SPORT brand, article number dpkv for VAZ 2110–2115 2112–3847010. The body is made of high-strength plastic, where there is a steel rod; the operation of the part is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Replacing the DPKV is carried out with the engine turned off. When installing, it is necessary to maintain the distance between the transmitting tooth of the disk and the sensitive element. For Lada, the minimum distance should be 1 mm, the gap can be increased to 1.2 mm.
The sensor comes with an adjusting washer, which must be used; the element will allow you to correctly adjust the gap when tightening the DPKV fastener bolt. If the driver independently changed the sensor, but did not adjust the gap, the ECU will receive an unstable signal, which will lead to uncoordinated operation of the internal combustion engine.
Experts recommend having a spare parts kit with you; the controller may suddenly fail, and the car will simply stall in the middle of the road. Replacing the sensor takes 5 minutes and does not require much experience or special tools.
Purpose
To control the engine and supply a spark at a certain moment and to the desired cylinder, a crankshaft position sensor is used. It detects the TDC position of the engine and then sends signals to the engine control unit, which sends a signal to the ignition module to supply a spark to the cylinder in which the compression stroke occurs.
The sensor is a rather important element and if it fails, the ECU will not be able to determine which cylinder needs to be supplied with spark and fuel.
Replacing chips and pinout of DPKV VAZ 2110
Over time, the wires going to the DPKV chip wear out. Located in the lower part of the engine and not far from the front wheel, as a result, dirt, snow, oil, and aggressive chemical media in the form of salt get on the DPKV and its chip and settle, which leads to slow oxidation of the wires on the chip and subsequently to their breakage. Since the wires from the chip are combined into a single bundle, when replacing it, a repair chip is provided with protruding two wires 15 cm long. Having removed the damaged chip, install a new one with a twist. The twist points are insulated using heat shrink or electrical tape.
From the diagram below it can be seen that their pinout is not complicated and two wires are directly connected to the signal input contacts in the control unit, passing along the entire length of the harness. The polarity of the connection between the signal wires of the sensor and the control unit must be observed. If the polarity is reversed, the synchronization system will not work. To restore the operation of the DPKV, you simply need to swap the wires and check the functionality by starting the engine.
Design
The sensor is a plastic part inside of which there is an electromagnetic element that operates on the Hall effect. A sensitive part protrudes from the sensor, which directly works with the master disk. The VAZ 2115 uses a generator drive pulley as a master disk, which has teeth for determining the position of the crankshaft by a sensor. The sensor is attached to the engine housing through an eyelet, which is pressed against the ebb on the engine using an M6 bolt. The sensor's power supply is shielded; this is necessary so that the signal reaches the control unit without interference.
Principle of operation
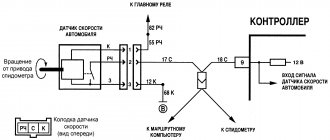
The operating principle of a modern speed sensor (hereinafter DS) is based on the Hall effect:
- The speed sensor transmits voltage pulses to the controller with a frequency directly proportional to the speed of the drive wheels.
- The controller, based on sensor pulses, regulates engine operation in idle mode, and with the help of the IAC (idle speed controller) controls the supply of air bypassing the throttle valve.
- In this case, the frequency of the DS signals is directly proportional to the actual speed of the car.
- DS differ in the connecting connectors to the harness block.
- BOSCH systems use a square connector.
- The sensor, which has a round connector, is used in systems such as GM and January 4.
- All of these sensors are six-pulse; they produce six pulses per axis rotation.
- A ten-pulse sensor is found in Samar carburetor trip computers.
Signals from the speed sensor are used by the control system to calculate fuel shut-off thresholds, and to electronically force limit the speed of the machine (in modern control systems). When installing the speedometer drive in models that still have one in the box, you need to be very careful, otherwise, when misaligned, the fragile plastic teeth on the speedometer drive drive gear will be crushed and then you will have to completely disassemble the entire gearbox (to replace the broken drive) and the cost of the issue increases . The output voltage for a low pulse level is permissible no more than 1 V, and for a high level it must be at least 5 V.
Symptoms of a problem
The crankshaft sensor has several characteristic signs of failure that clearly indicate its malfunction, but at the same time there are also signs that can be confused with other parts of the car engine.
If the DPKV is faulty, the car will show the following signs of breakdown:
- There is no spark;
- The engine does not start;
- One of the cylinders does not work;
- The car jerks when driving;
- Poor dynamics;
- Loss of power;
- Increased fuel consumption;
- The engine starts and immediately stalls;
- Doesn't start hot;
If there is no spark on the engine, this indicates a malfunction in the DPKV.
Examination
You can check the DPKV using diagnostic equipment using the ADC and multimeter channels. As a diagnostic device, you can use the ELM327 with the OpenDiag smartphone application; this assembly of the device and application allows you to determine faults in the car quite simply and is in no way inferior to professional diagnostic equipment.
Checking with a multimeter
Testing with this method consists of measuring the resistance of the inductor, which is located inside the sensor; most often it is the cause of sensor failure.
To carry out the check you must:
- Set the resistance measurement limit on the multimeter to 2 kOhm;
- Next, connect the multimeter probes to the terminals on the sensor;
- The readings on the multimeter should be in the range from 500 to 800 Ohms, if the readings agree, then the sensor is working;
- If the readings have a different range or the tester even shows 1, then this indicates a break in the inductor inside the sensor;
- In case of such a breakdown, the sensor must be replaced with a new one;
Error codes for DPKV malfunction
Using ECU self-diagnosis, you can check the operating status of all systems. For different cars, the checking principle is approximately the same. You need to connect certain contacts on the block for diagnostics. You can determine the malfunction by the blinking frequency of the “CHECK ENGINE” lamp
The most important thing when connecting contacts is that the ignition is turned off. And, upon completion of the test, you can remove the jumper no earlier than ten seconds after turning off the ignition
On a GAZelle car, the diagnostic block is located in the engine compartment. To check, you need to close contacts 10 and 12 of the diagnostic connector. Violations in the DPKV power system or in the sensor itself have code 53.
Replacement
To independently replace the DPKV on a VAZ 2115, you do not need to have great skills in car repair. You just need to prepare the necessary tools.
Replacement process
It is most convenient to carry out work from an inspection hole or overpass, but if one is not available, you can remove the right front wheel and unscrew the engine mudguard, after which free access to the sensor will open.
- Quite often, the sensor turns sour in its seat, after which it is difficult to get it out of there; to do this, you can use pliers and rotate the sensor to remove it;
- Before installing a new sensor, you need to clean the seat for easier installation;
- We assemble in the reverse order;
Location
The crankshaft position sensor (CPS) on the VAZ 2115 is located on the oil pump housing, namely, it has a special casting in the form of a bracket into which the sensor is installed and fixed in its position with a bolt. You can see the sensor by looking closer to the oil filter or from the inspection hole.
| Name / catalog item | Price in rubles |
| Injector 351.3847 ROMB | From 170 – 200 |
| 402.3837 AutoTrade | From 170 – 200 |
| 191.3847 (8 valves) | From 170 – 200 |
| 2112-3847010-04 | From 170 – 200 |
| EMZ 'Pegasus' 191.3847 | From 170 – 200 |
| Astro 27.3847 (8 valves) | From 170 – 200 |
| StartVolt VS-CS 0112 | From 170 – 200 |
| CTR Cartronic 2112-3847010-04 | From 170 – 200 |
| RepCom RK02004 (8 valves) | From 170 – 200 |
| Schetmash 2112-3847010 (8 valves) | From 170 – 200 |
Replacing the crankshaft position sensor on a VAZ 2113, VAZ 2114, VAZ 2115
Welcome! The crankshaft position sensor is needed in order to read the crankshaft revolutions and determine at what moment the pistons are at TDC (Top Dead Center), and thanks to it the controller (ECU) sends a spark and pours gasoline into the cylinder, thereby the fuel-air mixture in at a certain moment (When the pistons are at TDC) it burns out and the engine continues to operate smoothly and without interruption, but if you try to remove the sensor completely and start the car, or if you wait until it fails, then everything will be very sad, namely, the ECU will no longer understand at what point should a spark be supplied and at what point will it be necessary to pour fuel into the cylinder (the ECU simply will not know at what moment the pistons will be at TDC), thus the car will either terribly shake and the idle speed will twitch strongly, or it will simply not will start and by the way, this is the only sensor in the car, if which fails the car will no longer start.
Note! To replace this sensor on a car, you don’t need a lot of tools, much less time, it will be enough to stock up on: Socket heads and a wrench or a regular spanner wrench of about “10”, but in addition, if you want to check the sensor for serviceability, then in this In case, also stock up on a multi-meter, without which you will hardly be able to quickly check more than one sensor!
Summary:
Where is the crankshaft position sensor located? The sensor is located on a bracket and so that it does not dangle, it is screwed to this bracket with a bolt, and it is directed to the crankshaft pulley by which it understands what position the pistons in the cylinders are in at a certain moment, so that you can visually see the location of this sensor , look at the photo below, where it is shown approximately with a blue arrow and in detail with a red arrow.