A brake force regulator, or sorcerer in common parlance, is a mechanical device designed to relieve excess pressure in the rear drum brakes.
On VAZ-2109, VAZ-2108, VAZ-2114 and other front-wheel drive models produced in Togliatti, it was installed in the rear left part of the body, under the bottom, in front of the rear suspension beam. The brake pressure regulator on the VAZ-2107 model and other “classics” is located on the right in the direction of travel of the car.
New vehicles equipped with ABS and EBD do not use the sorcerer.
Pneumatic brake force regulator
The pneumatic regulator of the braking forces of a KamAZ vehicle, installed on the spar 7 of the vehicle frame, consists of an automatic regulator 2 of the lever 3, an adjustable rod 4, an elastic element 5, a compensator 7, connected by a rod 6 to the beams 8 and 9 of the vehicle axles. The mechanisms and available fastenings provide compensation for trolley distortions that are possible when braking on uneven roads. The elastic element protects the regulator from damage during vertical movements of the rear bogie axles, and also softens sharp shocks and reduces vibration.
Rice. Installation diagram of the brake force regulator: 1 - spar; 2 — brake force regulator; 3 — regulator lever; 4 - traction; 5 - elastic element; 6 — rod; 7 - compensator; 8, 9 — bridge beams; I — position of the regulator lever at the highest axial load (“loaded” vehicle); II - lever position at the lowest load (“empty” car)
Let's consider the design and principle of operation of the pneumatic brake force regulator.
Rice. Automatic brake force regulator: a - general view; b - design; 1 - valve; 2 - stepped piston; 3 - pusher; 4 — lever; 5 — membrane (diaphragm); 6 — ball heel; 7 - piston; 8 — pusher guide; 9 — inserts in the body; 10 — connecting tube; 11 — piston ribs; I, II - cavities; III - release into the atmosphere
For a loaded vehicle, lever 4 is in its uppermost position. When braking, compressed air enters cavity 1. Therefore, piston 2 will move down, and through tube 10, air from cavity I will enter the lower part and put pressure on the plunger-type piston 7, pressing the ball heel 6 to the pusher 3. When piston 2 moves down valve 7 moves with it, which, by means of a pusher, will first disconnect cavity II from the outlet to the atmosphere, and then move away from the piston seat 2. As a result, cavity I will connect with the outlet cavity II, and compressed air will flow through cavity II to the brake chambers of the wheels.
The insert in the body has inclined ribs I on which the membrane (diaphragm) 5 rests when the piston 2 is in the upper position. Piston 2 also has ribs 11. The lower the lever and the associated pusher go, the lower the piston 2 will go. Consequently, the working area will increase membrane 5 acting on piston 2.
When the lever is in the up position (at full axial load), the pushrod is also at the top. To open the valve, piston 2 must move down. When it moves slightly, the inclined ribs 11 of the piston 2 do not extend below the ribs 9 of the insert. In this case, the membrane rests only on the edge of the insert, and the force from it is not transmitted to piston 2.
When the lever is in its lowest position (lowest axial load), piston 2 must move downwards as much as possible to open the valve, since the pusher will also be in the lower position. In the case of maximum downward movement of piston 2, its inclined ribs will drop below the ribs of the insert. In this case, the active area of the membrane becomes largest. As a result, an air pressure will be established in cavity II approximately equal to 1/3 of the pressure at the inlet to the regulator.
When the wheels are released, the air pressure in cavity 1 will drop and piston 2 will move up. In this case, the valve will sit on the piston seat 2, separating cavities I and II, and will come off the pusher. As a result, compressed air from the brake chambers of the wheels of the middle and rear axles escapes into the atmosphere through cavity II and the hollow pusher, bending the edges of the rubber valve. And all elements of the regulator return to their original position.
The considered regulators adjust the pressure of the working fluid (air) to ensure simultaneous blocking of the wheels of the front and rear axles. In this case, proactive blocking of the front axle wheels occurs. However, this method of braking is not the most effective and safe from the point of view of maintaining vehicle stability when braking. In addition, excessive tire wear occurs.
Checking and adjusting brakes. Part 2
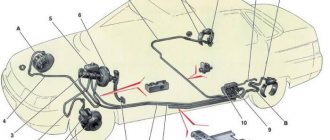
Rice. 6-11. Brake drive: 1
- main cylinder; 2 - tank; 3 — vacuum booster, 4 — brake pedal bracket; 5 — brake light switch buffer; 6 — brake light mounting nut; 7 — brake light switch; 8 — brake pedal
The brake pedal should “go forward” after starting the engine.
If the brake pedal does not “go forward”, check the fastening of the hose tip, the condition and fastening of the tip flange in the booster, the hose to the tip and the fitting of the engine intake pipe, since loosening the fastening or their damage sharply reduces the vacuum in cavity A and the efficiency of the booster.
Adjusting the brake drive
The free play of the brake pedal when the engine is not running should be 3-5 mm. The adjustment is carried out by moving the brake light switch 7 (Fig. 6-11) with nut 6 released. Install the switch so that its buffer rests against the pedal stop, and the free play of the pedal is 3-5 mm. In this position of the switch, tighten nut 6.
Adjust the brake pedal free play when the engine is not running.
If the brake light switch is too close to the pedal, it will not return to its original position. In this case, valve 21 (see Fig. 6-2), pressing against body 24, separates cavities A and B, which opens air access to chamber B, and the wheels are incompletely released when the pedal is released.
If moving the brake light switch cannot eliminate the incomplete release of the brake mechanisms, then disconnect the brake master cylinder from the vacuum booster and check the protrusion of the adjusting bolt 4 relative to the mounting plane of the master cylinder flange (size 1.25-o.g mm). This size can be set
holding the end of the rod with a special wrench, and using another wrench to tighten or unscrew bolt 4.
Adjusting the parking brake system
If the parking brake system does not hold the vehicle on a 25% grade when moving the lever 2-8 teeth of the sector, adjust the system in the following order:
— loosen the lock nut 7 (see Fig. 6-9) of the tension device and tighten the cable by tightening the adjusting nut 6;
— check the full stroke of lever 2, which should be 2-4 teeth per sector, then tighten the locknut.
After performing several brakes, make sure that the stroke of the lever has not changed and the wheels rotate freely, without sticking when lever 2 is completely lowered.
Checking the functionality of the pressure regulator on the car
Place the car on a lift or inspection ditch, clean the pressure regulator and its drive parts from dirt.
By external inspection, make sure that the pressure regulator and its drive parts are free of damage,
there is a leak of brake fluid, plug 24 (see Fig. 6-4) is recessed into the housing hole by 1-2 mm, there is no play in the connection of the earring 11 (see Fig. 6-3) with the elastic lever 10 and pin 15 of the bracket.
Have an assistant press the brake pedal. In this case, piston 2 (see Fig. 6-4) should extend from the body by 1.6-2.4 mm, compressing leaf spring 7 (see Fig. 6-3) until it stops against lever 5. Lever 5, overcoming the force from the elastic lever 10, it will rotate relative to the pin 4.
Non-compliance with the listed requirements, lack of piston stroke, as well as its insufficient or excessive stroke indicates a malfunction of the regulator or its drive. In this case, repair or replace the pressure regulator, and after installing it, adjust its drive (see chapter “Checking and adjusting the pressure regulator drive”).
Removing air from the hydraulic drive
Bleeding the brakes is necessary to remove air from the hydraulic drive, which significantly reduces the effectiveness of the service brake system. Air can enter the hydraulic drive due to depressurization of the system during repair or replacement of individual components, as well as when replacing brake fluid. The presence of air in the brake drive is indicated by increased travel of the brake pedal and its “softness”.
Before removing air from the brake system, make sure that all brake drive units and their connections are tight, clean the cover and the surface around the reservoir cover, fill the reservoir with Rosa fluid up to the “MAX” mark with the cover removed. Then thoroughly clean the bleeder fittings and remove their protective caps.
It is not recommended to use fluid drained from the system to fill the reservoir, as it is saturated with air, has a lot of moisture and may be contaminated.
Air from the system is removed first from one circuit, then from the other, starting with the rear brake wheel cylinders.
Place a rubber hose 2 onto the head of fitting 1 (Fig. 6-12) to drain the liquid, and lower its free end into a transparent container 3, partially filled with liquid.
By sharply pressing the brake pedal 3-5 times at intervals of 2-3 s, turn it off
ABS
The coefficient of adhesion between wheels and the road depends on the degree of their sliding, which varies from 0 (pure rolling of the wheel) to 100% (complete slipping or sliding when the wheels are locked). The maximum values of the coefficient of adhesion of the order of 10... 30% (depending on the road surface) will be when the wheels slip. Consequently, with this coefficient and degree of wheel slip, the greatest efficiency and safety of braking can be ensured. This is exactly what ABS provides.
All modern ABS are self-adjusting automatic systems. They include:
- wheel speed sensors
- electronic decision block
- pressure modulators
When ABS is operating, the signal from the wheel angular speed sensors is fed to an electronic decision unit, in which, in accordance with a given program, control signals are generated and sent to the modulator.
Rice. Diagram of the pneumatic ABS modulator (a) and its characteristics (b): 1, 5, 6 - valves; 2, 3 - electromagnets; 4 - piston; A—D—cavities; p—pressure; t — time
The figure shows a diagram of the pneumatic ABS modulator and its characteristics (change in braking force over time). ABS operation is accompanied by a multi-cycle process of automatically releasing and braking the vehicle's wheels. In each cycle there are phases of automatic release of the brakes, “holding” and braking (dashed lines in Fig. b) of the wheels. There are ABS in which a two-phase cycle is carried out (there is no “holding” phase). ABS operation ensures the required angular speed of the wheel and its sliding, corresponding to maximum traction characteristics.
Brake pedal sensor
The brake pedal sensor on Lada cars is involved not only in sending a braking signal to the car's brake lights, but also in regulating the air-fuel mixture.
As you know, vehicle emission standards are becoming stricter every year and manufacturers are forced to adhere to these criteria in order to bring their products to market.
The brake pedal sensor (BPS) is involved in the formation of the fuel mixture only on Lada cars equipped with the E-GAZ system. If in a car the accelerator pedal is driven by a cable, then the sensor is responsible only for turning on the brake lights when you press the gas pedal.
If there is a malfunction or incorrect adjustment of this sensor, the car will operate in emergency mode, which will be indicated by the “check engine” lamp and error number “P0504” will appear.
This article will discuss malfunctions of the brake sensor on Lada Granta cars, as well as its replacement and adjustment.
About the sensor
The DPT is a conventional “frog with two contacts” for making and breaking. There are no complicated electrical circuits in its design.
One of the contacts, which works to close, when you press the brake pedal, lights up the brake lights, which in turn signal the cars behind to brake.
The second contact, which opens when the brake pedal is pressed, opens its contacts and thereby sends a signal to the ECU to remove the load from the engine. This is necessary to reduce the fuel supply during braking, that is, driving at high speeds (above idle) and when you press the brake pedal, the car begins to stop, and at this time the sensor sends a signal to the ECU to reduce the fuel supply through the injectors to reduce speed and exhaust emissions in atmosphere.
The sensor is located on the pedal assembly under the steering column of the car, mounted on a plate with two nuts, and they are also used for adjustment and control tightening.
The cost of the sensor in an auto parts store is up to 300 rubles.
Causes of malfunction and their consequences
If there is an external or internal breakdown of the sensor on the Granta dashboard, the “Check Engine” will light up with error “P0504”. This error indicates a malfunction of the DPT.
Symptoms of a problem
- The car starts poorly and immediately stalls;
- The idle speed fluctuates;
- The motor does not develop the required power;
- Jerks when moving;
Reasons for failure
The main cause of DPT failure is the spring, which returns the sensor contacts to their original position. If the spring breaks, the contacts do not return and remain in the final position, thereby the ECU continues to receive a signal that the car is braking and thus does not allow it to develop the necessary speed to complete the maneuver.
Broken spring
A less common breakdown is the failure of the sensor housing, since the sensor is made of plastic, when removing or replacing it it is easy to damage it, which can harm its design and operating mechanisms.
And the last reason is carbon deposits on the contacts. When the sensor is used for a long time, electrical deposits appear on its contacts, which soon leads to a poor connection between the moving contact and the fixed one.
Carbon deposits on contacts
Before purchasing a new sensor, it is necessary to diagnose the DPT. It happens that the sensor nuts are unscrewed due to vibration and thus its adjustment is disrupted, which can result in an error on the dashboard.
Check sequence:
Check the connector contacts, make sure the connector has not come off the sensor;
Press the brake pedal by hand and release, make sure that the sensor stop returns to its original position, thereby confirming that the return mechanism spring is working.
Check the adjustment and tightening of the locknuts; with the brake pedal free, there should be a distance of no more than 0.5-1 mm from the sensor stop to the housing.
If any of these points are not met, you must begin replacing and adjusting the brake pedal sensor on the Lada Granta.
Operation of the pneumatic modulator
Let us consider in detail the operation of a pneumatic modulator made on the basis of an accelerator valve (Fig. a). Compressed air from the brake valve enters through the line into cavity A and then passes through cavity B into cavity C and presses down on the follower piston 4. The piston moves down and rests against valve 5, disconnecting cavity G from the outlet to the atmosphere. Further downward movement of the piston leads to the opening of valve 5.
As a result, compressed air begins to pass from the receiver through cavities D and D into the brake chambers.
If the braking wheel begins to lock, the electronic unit simultaneously sends control signals to electromagnets 2 and 3, which close valve 1 and open valve 6. In this case, cavities B and C are connected to the atmosphere - the wheel is automatically released. At some angular acceleration of the wheel, the electronic unit removes the electrical voltage from electromagnet 3. As a result, valve 6 closes again under the action of a spring and the holding phase begins.
The phase of repeated automatic braking of the wheel occurs when the wheel acquires a threshold angular acceleration. In this case, the electronic unit removes the electrical voltage from electromagnet 2, which allows valve 1 to open and connect working cavity B to the main line. Then the cycle repeats.
The principle of operation of a brake caliper and why it is needed at all
Welcome! A brake caliper is essentially a very necessary thing, since practically no car can do without it, because the brake caliper does the most basic work during braking, but not all people know how it works and what will happen if it doesn’t installed on the car, that’s what we’ll look at today.
Note! At the end, in addition to this article, there is an interesting video clip that shows the entire principle of operation of the brake system!
What is a caliper for and what is its operating principle?
In short, it is needed so that the car slows down when you press the brake pedal and if it is not there, as was said earlier, the car will not stop at all, since the main work of braking is performed by this particular caliper.
Well, if we talk in more detail and, in addition to all this, delve into the principle of its operation, then this very principle of its operation is as follows: when you press the brake pedal, pressure occurs in the brake system, namely the piston which is located in the master brake cylinder ( This cylinder is indicated by the number 3), moves from the beginning of this cylinder to the end, thereby still collecting a little brake fluid that is in the brake reservoir (indicated by the number 5), squeezing the brake fluid forward, it goes through the hoses and thereby squeezes out the pistons that are in the caliper itself, and these pistons press on the brake pads and the car stops.
Let's look at it in more detail, for this let's first look at what this main brake cylinder is, and it represents a structure inside which there is that same piston as well as a rod that presses on it, so when you have to stop the car, you press accordingly on the brake pedal, after pressing the rod will also mix forward, thereby the piston that sits on this rod will mix, and after mixing, all the brake fluid will be pushed forward, as it were, and it will go all the way to the working cylinders themselves, which we will talk about a little lower.
Note! Let us tell you right away so that you understand one thing, this brake fluid is not compressible, so if something does not press on it, it will also press on other parts of the brake system and at the same time it will not compress!
Now the fluid will press from one end, onto all working cylinders to which hoses are connected (Hoses that are connected to the working cylinders are indicated by numbers 2 and 4 in the photo above, which shows a diagram of the brakes of a VAZ 2110 car), so after the brake fluid is the working cylinder is filled, the piston which is located in this cylinder will be squeezed out and thereby put pressure on the brake pad, and the brake pad at this moment will compress the brake disc and therefore friction will occur which stops the car.
And in conclusion, let’s note why a car needs a brake reservoir, namely, thanks to the brake reservoir, which contains the fluid itself and maintains the normal level of this fluid in the system, to understand more, look at the photo located just below:
Where is the brake caliper located?
On many cars it is different, sometimes this caliper is located in the front part of the car, and sometimes in the front and rear at the same time, and on some cars (Mainly on old ones) there were usually no brake calipers at all, and instead of them ordinary drum brakes were used , and these brakes heat up very quickly and therefore the effectiveness of their braking after constantly pressing the brake pedal (Especially in hot weather) greatly decreased and thus the number of accidents was not small.
Note! On domestically produced cars (VAZ), in most cases, the brake caliper is located only at the front of the car, and the rear wheels are equipped with conventional brake drums! (By the way, if you are interested and want to know how brake pads for disc and drum brakes work, then read an interesting article entitled: “What are brake pads and how not to run into a fake?”, everything is described in detail there)
Links! How to replace the front brake caliper - on a classic? How to replace the caliper on a VAZ 2108-VAZ 21099?
Additional video clip: You can learn more about how the brake system works in an interesting video clip located just below:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Av-jj8NNrv8
Vaz-Russia.ru
Integrated Active Safety Systems (ISAB)
Currently, domestic integrated active safety systems (ISAB) have been developed, forming a complex of ABS and PBS.
Unlike ABS, the traction control system installed in ISAE ensures the required wheel movement not in braking mode (as when ABS is operating), but in traction mode. The fact is that when the car moves, including when maneuvering on a road with different adhesion properties of the surface areas interacting with the drive wheel, different slipping occurs. This can lead to a loss of motion stability, for example, when accelerating a car, when excessive traction may be supplied to the wheels, unbalanced by the traction capabilities of the “wheel-road” pair. The action of PBS, unlike ABS, is based on the fact that in the event of slipping of the vehicle’s drive wheel, the system provides a reduction in traction force on this wheel. This prevents wheel slipping and increases vehicle stability. As a rule, the operation of the PBS is based on reducing the fuel supply to the engine, i.e. comes down to reducing the traction force on the slipping wheel(s).
The main task of regulators and the physics of braking
Why is the brake pedal on a VAZ 2110 tight?
The adhesion force of a car wheel to the road surface, like the friction force, is proportional to vertical loads. The proportionality coefficient is considered to be the coefficient of the tire's level of adhesion to the road. This value does not depend on the person in any way. It can be determined based on the condition of the road and tires. The higher the adhesion of the wheel to the asphalt surface during braking, the less will be And since when the pads operate, inertia also acts on the car, the vertical load on the wheels is redistributed. Therefore, the force on the disk should be uneven. The brake force regulator is also used to improve braking efficiency when the machine is not loaded. In this case, the traction force will be completely different than in the case of a loaded car.
Possible malfunctions of the regulator
In general, there are few malfunctions that can occur in the sorcerer. These include:
- Valve jamming;
- Misalignment of position;
- Brake fluid leaks.
A deregulated sorcerer can be adjusted. You can determine the need for adjustment by the behavior of the car when you press the brake. If the regulator is set incorrectly, the car starts to toss to the side.
If the valve jams or fluid leaks, the mechanism must be replaced. Theoretically, it can be repaired. However, the process of such repairs is complex and expensive, which makes it unprofitable.
The feasibility of installing a vacuum brake booster
The vacuum booster dramatically improves the driving comfort of the VAZ 2108. It reduces the pedal effort required to stop the car. All modern cars are equipped with a vacuum booster. Domestic and imported. Nowadays, it is impossible to imagine a car without a vacuum brake booster.
The amplifier is aggregated with the master brake cylinder and is mounted on a shield separating the engine compartment from the interior of the VAZ 2108. It is connected to the engine crankcase with a flexible hose to supply rarefied air necessary for the operation of the amplifier. A malfunction of the amplifier is clearly indicated by a noticeable increase in the force on the brake pedal. Braking acceleration decreases.
Continuing your trip with a broken amplifier is very risky.
You can drive to the nearest car service center with caution. A cracked hose can be wrapped with several layers of electrical tape. If replacing a cracked hose and check valve does not produce results, the unit must be replaced
If replacing the cracked hose and check valve does not produce results, the unit must be replaced.
Work on removing the amplifier is carried out in this order.
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal. De-energize the electrical system.
- Disconnect the wiring block from the hydraulic reservoir cap located on the brake master cylinder body.
- From the passenger compartment, remove the amplifier pusher pin using pliers. Disconnect the pusher.
- Disconnect the hose going to the engine crankcase.
- Unscrew the two nuts securing the brake master cylinder.
- Move the cylinder away from the amplifier housing. Leave it hanging from the metal hydraulic pipes.
- Unscrew the four nuts securing the amplifier bracket to the engine shield and carefully remove the amplifier.
- Unscrew the two nuts securing the amplifier to the bracket. Disconnect the bracket and amplifier.
Install the new VAZ 2108 vacuum booster in the reverse order.
Setting the brake force regulator
Adjustment of the sorcerer should be done on an overpass or inspection hole. At the same time, the car is unloaded and driven to the work site. To perform the manipulation you will need:
- Socket wrench 13 or corresponding socket;
- Drill diameter 2 mm.
To adjust the sorcerer, use a wrench to loosen the bolt securing it to the lever bracket. Next, use a screwdriver to move the bracket until the resulting gap allows you to insert a prepared two-millimeter drill into it. After this, the bolt is tightened.
Note: the brake pressure regulator of the VAZ-2110 and previous VAZ models turns sour during operation so that it is not possible to move its bracket. In such a situation, you should pour WD-40 liquid over the rusted area, wait 15-30 minutes, and then use a hammer to move the part to the side using a soft drift.
How to regulate RTS
If we take VAZ cars, then the adjustment of the brake force regulator greatly depends on the position of the body. The adjustment must be performed not only during each maintenance, but also when replacing suspension parts - springs or shock absorbers, after repair work on the rear beam and when replacing it. To set up, the car must be placed on an overpass. This is done not only for ease of operation, but also to install the suspension in a balanced position. In this state, when you press on the trunk with your hands, the car will rock two or three times. So, to set up, you first need to loosen the fasteners to the bracket. It is necessary to achieve a gap of 2 mm between the elastic plate against which the rod rests and the lever. This is done by moving the mechanism.
It must be taken into account that in the process you will have to overcome the resistance of the spring. They are quite large, so it is recommended to use a special tool or other suitable device. Then the bolts are tightened and the gaps are checked using a feeler gauge. If there is no such tool, then you can use a drill with a diameter of 2 mm or a suitable coin.
Replacing the brake pressure regulator
The replacement of the sorcerer on VAZ-2110 cars and other vehicles equipped with an RTD is carried out on an overpass. You need a 13 mm spanner, a powerful screwdriver and a special 10 mm wrench designed for unscrewing brake pipes. Before starting work, the assembly must be cleaned of dirt and rust, doused with WD-40 or another penetrating compound, and then wait half an hour.
Work begins by unscrewing the bolt securing the bracket to the spring. Afterwards, the brake pipes are dismantled, the position of which is recommended to be pre-marked.
You can also unscrew the tube fittings with a regular wrench. However, using a special tool makes the job easier and reduces the likelihood of “licking” the edges. After the fittings, unscrew the two bolts securing the sorcerer to the body and remove the part. It is necessary to install the new VAZ-2110 sorcerer in strict reverse order. After installing it and before adjusting the RTD, you should bleed the rear brake circuits. Next, the above-described procedure for setting up the sorcerer is performed.
Replacing the sorcerer on a VAZ 2114
Reasons for VAZ 2110 battery discharge
Dismantling and reinstalling a non-working device does not cause significant problems and is accessible to almost anyone. The automaker recommends replacing the faulty regulator assembly. To carry out the work you will need:
- flat screwdriver;
- key to 13;
- 10mm socket for removing brake pipes.
The replacement sequence is as follows:
- We provide convenient access to the rear of the car's underbody (we use a lift, pit, or overpass).
- We find the regulator drive lever. We lift the bracket up and release it. If difficulties arise, use a screwdriver to slightly release the bracket.
- Remove the earring bracket.
- Now we disconnect the four tubes from the body of the product. To do this, you need to loosen and unscrew the fastening nuts. To prevent brake fluid from leaking, plug (seal) the holes of all pipes. In the future, in order not to confuse the connections to the regulator, we mark the 4 pipes with different colors or numbers.
- We unscrew the front bolt of the sorcerer (with which it is attached to the bracket).
- From the side of the bracket, unscrew another bolt.
- Remove the complete device (together with the drive).
- After replacing the product, installation is carried out in the reverse order.
Please note that after reinstallation, the earring fastening bracket must be crimped with pliers. In addition, it is necessary to bleed the brake system and adjust the device for proper operation.
Examination
The operation of the VAZ-2109, 2110 and other AvtoVAZ models is checked on the move, in closed areas. To do this, accelerate the car to a speed of 40 km/h and sharply press the brake. The rear wheels should lock 1/2 second later than the front wheels.
The wheels are monitored by an assistant located outside the car. If wheel locking occurs noticeably later or does not occur at all, and also if the rear axle is locked simultaneously with the front, the sorcerer adjustment procedure is repeated.
To increase the response time of the rear brakes, the gap between the adjuster and the bracket is increased; to shorten it, it is reduced accordingly.
VAZ 2109: adjusting the brakes yourself is easy and simple
Adjusting the brakes of the VAZ 2109
When the car starts to move away, you often get the feeling that someone is holding it from behind. You need to stop and check the temperature of the rear drum with your hand. If it is heated, therefore, the rear pads jam when braking. Conclusion: it is necessary to adjust the brakes on the VAZ 2109. On a VAZ 2109, adjusting the rear brakes is not difficult. For this reason, repair and inspection work must be carried out to adjust the free play of the brake pedal. Free play adjustment is carried out in the garage. Before starting repairs, you need to check the condition and operation of the rear brake system.
About Brake Force Controllers (P-Valve)
There is a belief that when converting rear drum brakes to disc brakes, it is also necessary to change the brake force distributor (aka P-Valve) to a regulator from cars with rear disc brakes (RDB). Moreover, in the terminal stage, this postulate looks like “install any car with rear disc brakes.” Since such advice smacks of technical idiocy, and the integrity of the skin depends on the brakes, it was decided to deal with this issue.
Here it is, the classic Toyota brake force regulator:
Regulator for cars with ABS
This is a regulator for cars with ABS. On cars without ABS, it is the same shape, but in the place where the yellow mark is in the photo, there is another outlet for the brake pipe (which is directly connected to the left input in the photo).
"Wizard" OR ABS?
And yet, such a regulator on a modern car is a legend of deep antiquity. It cannot compete with ABS, especially if the driver is an average driver who does not know extreme driving techniques. The curb weights of Kalina and Priora are almost the same - the difference is less than a percent. Using the same tires that were on the Kalina, the Priora with ABS showed the best results under any load. Moreover, no dosing of force on the brake pedal was required, you just press with all your heart, and the electronics do the rest.
Test results:
Adjusting the braking forces of Lada Vesta
The operating principle of the system that regulates and distributes brake fluid pressure on Lada Vesta cars is fundamentally different from previous models. The Lada Vesta brake pressure regulator is directly connected to the ABS system and is electronically regulated depending on the speed of each wheel.
The ABS control unit transmits signals from speed sensors and analyzes the situation. The electronics itself detects all faults and reports them to the driver using a special lamp on the dashboard.
Service
This part cannot be repaired. But in order for it to work properly, it needs to be maintained. This is usually done before making adjustments. The unit is installed in an unfavorable location - during operation it gets exposed to water, snow, dirt, and reagents from the road. All this makes the job worse. Gradually, water and snow become causes of corrosion.
General maintenance activities include cleaning the “sorcerer” from rust, removing the old rubber boot and installing a new one, replacing the lubricant, and cleaning all elements of the regulator from contamination. The old grease is first removed from under the boot.
Adjusting the “sorcerer” on “Logan”
The brake force regulator on the Logan is located on the bottom between the front and rear axles.
To self-adjust, you need to clean the “sorcerer” and replace the lubricant in it. Then make half a turn with the adjusting nut. Then you can go for the test. If the rear pair of wheels does not brake, then tighten the nut again.
If the vehicle being tested does not have ABS, then even if you tighten the nut all the way, you may not achieve the result. Sometimes replacing the sorcerer can help, but this does not always save the situation. The fact is that in 9 out of 10 Logans without ABS, the regulator does not work at all. The reasons are a weak spring. And the owner has two options - change the springs to stiffer ones or install a rubber gasket to increase the pressure on the “sorcerer” mechanism.
FakeHeader
Comments 28
And what tubes should be connected to each other? Can I have a diagram?
Honestly, I can’t answer you exactly, since I already bought one, and just when I changed the hoses for iron, I connected them as they were, who knows how it is, because they have circuits arranged on the GTZ, where is the back where is the front, I got it right now, not cross to cross, as in stock, but the front, rear, and GTZ will be changed in the same way as it was, I’ll connect everything, I want from the new Niva, VUT and GTZ) in general it will be superb, I’m waiting for my system to run out)
This means that the tubes on the GTZ have been swapped as well.
maybe x.z. I can’t say anything, but I think it certainly won’t get worse)
The sorcerer threw it out. When pressed smoothly, the butt grips faster. I read on the drive that it is also necessary to swap the circuits on the GTZ.
I didn’t notice anything like that, I didn’t even know that I didn’t have a sorcerer))) until I decided to check just because I don’t care about making rear brake pipes)) when I press it smoothly, it slows down as usual, when I press it hard, the car, according to passengers, gets stuck, but I still want something better, here and the GT from the new modernized Niva, in my plans, I really want it, but I live in Tatarstan, in a small town, where the evil, despicable garbage ((( will get along with the car
I haven't seen a car yet. And your front discs are perforated and notched. If so, what kind of pads do you use?
Yes, these are the wheels, Alnas, ATE pads, starting from the rear)
And what tubes should be connected to each other? Can I have a diagram?
Nobody suggested a diagram? otherwise I want to throw out the sorcerer, but I can’t find which tube to connect to which anywhere
Nope. But I think so.
Nobody suggested a diagram? otherwise I want to throw out the sorcerer, but I can’t find which tube to connect to which anywhere
Connect the tubes to each other. UAZ would be harmful
Nobody suggested a diagram? otherwise I want to throw out the sorcerer, but I can’t find which tube to connect to which anywhere
The adapters are there. I think I'll throw out the sorcerer in the summer. Just take an adapter so that there are threads on both sides M10×1.25
I understand that you can unscrew all 4 tubes from the sorcerer, of which 2 come from the GTZ and 2 are connected to the left and right rear wheels through the same adapter: GTZ tube - left rear tube, GTZ tube - right rear
essentially the same as in the picture
Yes. There on the sorcerer itself there are arrows for entrances and exits
Damn, here you are))) I didn’t notice)))
How would I notice it? ))) the car brakes better than stock. Eee, but I thought it would come from 14th ventilated, perforated, brake discs and good pads, but it turns out I don’t even have this extra junk) it turns out that now I need to pump both rear brakes first, then both front ones, or vice versa, but not according to the book crisscross)
Haven’t you looked under the car even once in all this time? Have you looked at the condition of the bottom/sills and brake pipes?
Well, I wrote that I regularly climbed under the car, but didn’t look specifically at the place of the sorcerer)) there are some cuts from the factory crap, like anti-corrosion on the bottom, I regularly inspect, lubricate, bitumen mastic with anti-corrosion agent, tightened the handbrake a couple of times, changed the fuel filter, but that’s exactly what I didn’t look closely at this place)) I noticed what I already wrote only because I decided to look at the hoses that go to the beam)), because one of the front ones was completely sad)
Regulator device on KamAZ vehicles
This unit consists of a valve, a valve pusher along with an actuator. The device also has a piston with an inclined rib, a membrane that is in connection with the piston. There are connecting tubes inside the housing. The adjuster channels attach to the top of the faucet, and a second channel connects to the brake chambers on the rear wheels. When the car slows down, air supplied from the top of the brake valve to the first channel of the regulator moves the piston down, and on the other side it is compressed until it stops. The valve is pressed against the pusher seat and the second channel at this moment is more connected to the atmosphere. Further movement of the piston will then cause the valve to open. Air from the first channel will flow into the second, and then to the brake chambers.
The MAZ brake force regulator has a similar device and operating principle.
Mechanism design
The Sorcerer is the ancestor of the modern ABS system.
The device consists of a housing, pistons, and valves. The body inside is divided into two cavities. The first interacts with the main brake cylinder. The second is connected to the rear brake mechanisms. When performing emergency braking, when the front part of the car tilts, using pistons and valves inside the regulator, the access of fluid to the rear brake mechanisms is blocked.
In this way, the force on the wheels of the rear axle is automatically controlled and distributed. The distribution of forces depends on how the axial load changes. Automatic sorcerers speed up the process of unlocking the rear wheels.
"Chevrolet Niva"
In the normal position of the regulator, as the vehicle's weight increases, its braking distance decreases - this affects the more complete use of the traction weight by the rear wheels.
The best braking is at full load, when the regulator minimally limits the pressure in the rear brakes.
But at partial load this is fraught with skidding. The high center of gravity and short wheelbase of the Shnivy contribute to a significant redistribution of mass during braking, therefore, at partial load, the contribution of the rear axle to braking is small.
How to tighten the handbrake on a Prior? The auto industry breaks down as always - Fix the Car!
If the handbrake on a VAZ-2112 becomes difficult to hold, then you should not change it immediately, since the cable can be adjusted. If the mileage on the car is high, the rear pads on the car may wear out. This may reduce the effectiveness of the handbrake and the entire braking system. In this case, the handbrake cable will need to be tightened.
Handbrake diagram for VAZ-2112
For clarity, here is a diagram of a hand brake
1 - button that fixes the handbrake lever; 2 — hand brake lever; 3 — protective cover; 4 — handbrake rod; 5 — cable equalizer; 6 — adjusting nut; 7 - lock nut; 8 - cable; 9 — protective sheath of the cable.
In this scheme we need element number 6. It is he, and only him!
What is required for adjustment?
In order to adjust the handbrake you need a platform or lift. If there are no such devices, then you can simply hang the rear wheels on the “goats”. They can be installed under the car using a jack. It’s also worth taking two “13” keys and pliers.
Start:
- The car is installed on an overpass or “goats”. Hanging out your butt
- The lever position is set to the lowest possible position. We put the handbrake at the very bottom. Do not pay attention to the scuffs of the console; we conducted an experiment with non-standard armrests. The iron fastenings of the armrest are visible. The photo shows the editorial car
- Use a wrench to loosen the locknut. Adjusting nut
- The second wrench holds the adjusting nut.
- The adjusting nut should be tightened until the cable is tensioned. It must be remembered that the rod should be held with pliers when tensioning the cable. Tighten the adjusting nut
- After this, you should make sure that the full stroke of the handbrake lever is no more than 4 and no less than 2 clicks.
- When the stroke check is completed, the locknut is tightened. The adjustment is held with another key.
- If necessary, change the mechanism to a new one. Everything is rusty, we changed the adjustment mechanism
- After releasing the adjusted lever down, you should spin the rear wheels. When the lever is in its lowest position, the wheels should spin freely.
THIS IS INTERESTING: How to set the ignition of a VAZ 21099
If you cannot tighten the cable, then it should be replaced with a new one.
Adjusting the handbrake after tensioning
After adjusting the brakes, you need to check them again. To do this, the car should be placed on a road with a slope of at least 23%. The car should be in neutral gear in this area and with the handbrake pulled up. If the handbrake brakes hold the car in this area, then the handbrake is adjusted correctly.
What to do when adjustment does not work
There are also cases when the above actions are not enough to adjust the handbrake. This can happen, for example, when the handbrake cable is broken. This happens on the VAZ-2112, although rarely. In such situations, the cable must be replaced. The cable also needs to be replaced when:
- The tips are loose.
- The cable itself begins to stretch, which will lead to its breakage during operation. HAIKU! The old cable is very worn out! For comparison, old and new handbrake cables
- Physical wear (scuffs and cracks) of the handbrake cables. Heavy wear on the handbrake cable
- It is quite difficult for the cable to move in the casing even after lubrication.
This replacement procedure does not require contacting a service station. Although this will require some time and skills from the driver, such work can be done independently.
It should also be remembered that when replacing the cable, certain conditions must be observed. To do this, the driver will need an assistant who will pull the cable.
Why do you tighten the handbrake?
The cable acts here as a drive. If the driver pulls the handbrake lever, then at the same time he uses the cable, which spreads the pads in the rear wheel.
If the handbrake is faulty, you just need to tighten the cable or replace it with a new one. On a VAZ-2112 it’s quite easy to do this with your own hands.
Need for adjustment
You can determine that the parking brake needs adjustment when checking. It is recommended to do it every 30,000 kilometers. This procedure should be done even if the handbrake seems to be working well.
The device must also be checked in cases where it does not work. For example, a car moves when the brake lever is applied.
How to install a tee instead of a sorcerer
In the case of the VAZ 2106-07, you can simply remove the regulator; the tee is already installed in the system; the main line from the GTZ is simply connected to it.
- Using a special “10” wrench, unscrew the brake pipe fittings from the mechanism.
- Unscrew the tube coming from the brake adjuster from the rear brake hose.
Disconnect the sorcerer tube from the rear brake hose
- Disconnect the control lever from the axle and body. We take out the regulator assembly with the rod and throw it away.
- Carefully bend the brake pipe from the master cylinder to reduce its length. It should not dangle under the bottom of the car. We connect it to the brake hose of the rear brakes.
bend the brake pipe from the master cylinder to the rear brake hose
Now all the force from the main one goes through the tee to both rear brake cylinders. Therefore, deceleration will occur on both wheels simultaneously with the front ones.
What is a “sorcerer” and why is it not found on modern machines
Many car owners do not even suspect that their car has a tricky and extremely important part on which safety directly depends.
The “sorcerer” is popularly called the brake force regulator for the rear axle of a car. This device is embedded in the brake system and is located under the bottom of the car, on the body near the rear axle, so it is not so easy to detect. The component has many names - “hydraulic braking torque regulator”, “braking force regulator”, “hydraulic pressure reducing valve”. The device received the strange name “sorcerer” for its secrecy, inconspicuousness and mystery.
The car needs a “sorcerer” to control the pressure on the rear brakes. When braking, the front and rear axles of the vehicle are loaded differently, and the force required to effectively brake the vehicle on both axles requires dynamic correction. For these purposes, a brake force regulator is needed.
“Sorcerer” does not allow the rear, unloaded wheels to lock before the front ones, thereby eliminating the danger of the car drifting into an uncontrolled skid. The presence and serviceability of the “sorcerer” is especially important for models equipped with drum brakes.
All mechanical pressure regulators in the hydraulic brake system are divided into two types - controlled and uncontrolled. The former are able to independently change the pressure in the brake mechanisms of the rear wheels depending on the intensity of braking and the load on the axle. The latter are deprived of a rigid connection with the car’s suspension and simply release pressure in the hydraulic system of the rear brakes when a certain threshold is reached through a special valve.
Active, or controlled, pressure regulators during operation take into account the distance between the rear axle and the bottom due to the presence of a rigid connection with them. When braking sharply, the car nose-dives, the distance between the rear axle and the bottom increases, the lever from the axle releases the piston, it moves and blocks access to the brake fluid to the rear wheels - they continue to spin and are not blocked. When the car is heavily loaded, the brake force regulator may not work at all - the load does not allow the body to rise and the mechanism does not turn on.
When so-called spacers are used in the rear suspension design, the “sorcerer” can also turn off completely - it perceives the increased distance between the rear axle and the body as an emergency situation and “releases” the rear brakes.
Due to the relatively low load on the rear part, when braking, it is the rear wheels that will lock first, which will greatly increase the risk of losing control of the car even with a minimal deviation from the straight trajectory.
Removing the “Sorcerer” from a vehicle is strictly prohibited. If it is excluded from the brake line, the vehicle is braked synchronously by all four wheels, which guarantees inadequate vehicle behavior on unstable surfaces and when deviating from straight-line motion.
The age of this device ended exactly when cars began to be equipped with an ABS system and its more advanced versions. Unlike the “sorcerer”, electronic brake force regulators take into account many more parameters, namely, they have feedback with each specific wheel of the car. They not only reduce and increase the pressure in the hydraulic drive, but also take into account the coefficient of adhesion of the tires to the road surface.
How it works
The design of the regulator consists of a lever that is attached to the rear axle and the “shaman” itself. Through this lever (torsion bar) the angle of inclination of the rear of the car relative to the ground is transmitted, respectively, the degree of pressure on the piston. The more the car is pressed, the more it is loaded, the more the piston is pressed - more pressure goes to the rear pads. The diagram below shows how to connect the regulator to the car body and axle.
The regulator itself consists of:
- Housings
- Traffic jams
- Piston
- Piston return spring
- Two fittings to which the brake system pipes are connected. The lower one is supplied with pressure from the master cylinder, the upper one is supplied with a line to the rear brakes.
"LADA KALINA"
We set the regulator so that the rear is slightly late in locking the wheels. With this setting and partial load, the car needed only 27 m to stop. Fully loaded - 29.5 m. There are slight difficulties in preventing the front wheels from skidding. We reduce the gap in the regulator to zero - the half-empty Kalina stops after 31.8 m. The braking distance increases by 4.8 m, accompanied by a sharp blocking of the front wheels. The loaded one slows down after 35.2 m, the deterioration is even greater - 5.7 m! The pedal effort is increased and the brakes become noticeably hot.
Now we move the adjuster so that the rear brakes work as efficiently as possible. At partial load, the rear wheels suddenly lock and the car drifts off course—you have to release the pedal. On the verge of blocking it is very difficult to brake. The result is 30 m, which is 3 m worse than the “norm”. Full load gave a result of 26.9 m, which is 2.6 m better than the base (29.5 m). There are no comments regarding deceleration control. At the basic position of the regulator, the braking distance increases with increasing load. At partial load the spread of results is 4.8 m, so the base position is most effective. When you deviate from it in any direction, the braking distance increases.
- On a fully loaded vehicle, depending on the position of the regulator, the spread of the braking distance is 8.3 m.
- The best results, as on the Niva, come with increasing pressure in the rear brakes.
- However, on a slippery road, even in smooth turns, early locking of the rear wheels is possible, leading to a skid.
- And at partial load, with the regulator position different from the base one, the braking distance only increases.