How many kg of aluminum are in the VAZ 2106 engine?
How we are working
| VAZ model | Car weight | Blockage |
| 2105 | 955 kg | 30% |
| 2106 | 1045 kg | 30% |
| 2107 | 1060 kg | 30% |
| 2109 | 945 kg | 30% |
Interesting materials:
What is the difference between cabbage soup and green borscht? How to remove hair dye from a case? How to remove soap stains on glass? How to clean the outside of a stainless steel kettle? How to clean the floor from silicone? How to clean silicone from the toilet? How to remove sticker marks? How to clean the inside of a thermos from tea? How to remove iodine from clothes? How to remove red wine from white jeans?
Disadvantages and advantages
The 2106 engine has significant disadvantages:
- excess heat is removed in the piston crown well and in fins with steel adjusting plates inside the studs;
- dynamic loads are reduced due to the displacement of the finger to the right from the axis of symmetry;
- When assembled into an engine, the pistons are installed with markings in one direction, which increases labor costs and human error.
The internal combustion engine uses a model 2103 cylinder head, a 35.3708 starter and a G221 generator for a 42A engine. Oil consumption does not exceed 700 g / 1000 km. The operating instructions indicate that it is recommended to add 200 ml of lubricant less than the volume of the entire system. Markings for filling oil are shown in the table above.
Characteristics of ICE 2108
German designers built a small amount of power into the engine, sufficient for a three-door hatchback weighing less than 1 ton. The timing drive again became a belt drive, but the shortcomings of the previous generation 2105 were taken into account. The existing cooling system was ideal for a small engine; replacing it was not practical in terms of cost.
ICE 2108 has advanced technical characteristics for its time:
Design Features
The motor is cooled in a closed loop by circulating coolant. The operating principle of the cooling system is forced.
The operation scheme of the lubrication system is combined - splashing plus supply of engine oil under pressure.
The operating order of the cylinders is as follows: 1—3—4—2.
The internal combustion engine device allows for major repairs of the VAZ 2106 engine and additional tuning of the VAZ 2106 engine.
The VAZ 2106 engine is replaced after familiarization with the new prices for this type of engine. Before you start replacing the engine, you need to find out how much the VAZ 2106 engine weighs.
The power unit of the sixth model is installed on VAZ 21074, NIVA, VAZ 2106 vehicles. UAZ vehicles are not equipped with these engines.
Cylinder block
The cylinder block is its own, marked 2106-1002011, cast from high-strength cast iron, differs from block 2103 only in the increased cylinder diameter.
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Material | Ductile iron |
| Cylinder diameter, mm | 79,0 |
| Intercylinder distance (distance between the axes of adjacent cylinders of the block), mm | 95,0 |
| Block height (distance between the upper plane of the block and the axis of the crankshaft), mm | 215,9 |
| Diameter of boring of crankshaft supports (for main bearings), mm | 54,52 |
| Weight, kg | 39,200 |
Maintenance Procedure
The classic internal combustion engine device allows you to perform simple actions when servicing the engine:
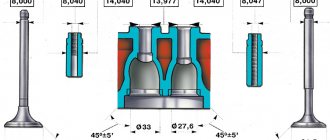
| Valve seat | width 2 mm, angle 45° |
| Camshaft | upper inside cylinder head, phase width 232°, exhaust valve advance 42°, intake valve retard 40° |
| Camshaft oil seal | diameters - 40 mm, 56 mm, width 7 mm |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| Cylinder diameter | class A - 79 - 79.01 mm |
| Pistons and rings | Tinned aluminum alloy piston |
| Piston diameter | class A - 78.94 - 78.95 mm |
| Liquidation | piston / cylinder wall - 0.153 - 0.173 mm (standard) or 0.19 mm (maximum) |
| Upper compression ring | 1535 - 1555 mm |
| Bottom compression ring | 3.957 - 3.977 mm |
| Oil scraper ring | 2015 - 2035 mm |
| Gap between piston groove and ring | 0.03 - 0.07 mm |
| Motor shaft | cast iron, casting |
| Number of main bearings | 5 |
| Gear journal diameter | 50.795 - 50.775 mm |
| Major revised resolution | 0.1 - 0.5 mm |
| Connecting rod bearings | shaft pin diameter - 47.814 mm |
| Crankshaft oil seal | front - diameters 42 mm, 60 mm, width 7 mm |
| Piston stroke | 80 mm |
| Fuel | AI-92 |
| Environmental standards | Euro 2 |
| Fuel consumption | highway - 7.8 l / 100 km |
| Oil consumption | no more than 0.7 l / 1000 km |
| Oil for 2106 | 5W-30 – 15W-40 |
| Engine oil volume | 3.75 l |
| Replacement frequency | every 55,000 km |
| Working temperature | 80° |
| Motor resource | stated 120,000 km |
| Valve adjustment | nuts and dipstick |
| Cooling system | forced |
| Refrigerant quantity | 9.85 liters |
| water pump | polymer impeller, block mounting |
| Turn on | distributor |
| Spark plugs for 2106 | A17-DVR, FE65CPR, A17DV-10 |
| Gap between spark plug electrodes | 0.5 - 0.6 mm |
| Valve circuit | double-row roller, 114 links |
| Cylinder order | 1-3-4-2 |
| Air filter | drying with replaceable cardboard cartridge and pre-filter, temperature adjustment depending on the season |
| Oil filter | recommended Mann W914/2 |
| They're flying | 129 teeth, 0.62 kg |
| Flywheel bolts | 10x1.25 mm, length 23.5 mm, |
| Valve stem seals | Manufacturers Horse or Corteco |
| Compression | cylinder pressure from 10 to 14 bar, pressure drop in individual cylinders within 1 bar |
| Oil temperature | 80°C |
| Thermostat temperature | 80 - 84 ° C |
| Pressure valve inside the radiator cap | 0.7 - 1 bar |
| Contains in the release of harmful products | CH-1 |
| Clamping force of threaded connections | spark plug - 31 - 39 Nm |
| Service element | Time or mileage (whichever comes first) |
| Timing belt | replacement after 100,000 km |
| Battery | 1 year / 20,000 |
| Valve clearance | 2 years / 20,000 |
| Crankcase ventilation | 2 years / 20,000 |
| Belt guide accessories | 2 years / 20,000 |
| Fuel line and tank cap | 2 years / 40,000 |
| Engine oil | 1 year / 10000 |
| Oil filter | 1 year / 10000 |
| Air filter | 1-2 years / 40,000 |
| Fuel filter | 4 years / 40,000 |
| Heating/Cooling Fittings and Pipes | 2 years / 40,000 |
| Coolant | 2 years / 40,000 |
| Oxygen sensor | 100 000 |
| Candle | 1-2 years / 20,000 |
| Exhaust manifold | 1 year |
As the effective life of an internal combustion engine increases, consumables can be replaced more often than the specified periods, or operations for cleaning the carburetor, engine, jets and other accessories can be added.
Tuning rules
The main goal of high-quality tuning is improved engine performance. And the desired result can be achieved using the following methods:
- boosting the engine;
- chip tuning;
- replacing the ignition system with a more powerful one.
The most difficult and one of the most expensive procedures is increasing the diameter of the cylinders and the piston stroke. The weight of the VAZ car does not change, but the output power increases significantly. The best solution in this case is to replace the cylinders, which will be both easier and cheaper to install. The overall dimensions of the components will change very slightly and will not affect the ride quality in any way. Dimensions make themselves felt only when the vehicle is overcrowded or faulty.
Another effective tuning method is to improve the dynamic performance of the engine, achieved in the following way:
- the weight of the crankshaft and connecting rod-piston system is reduced;
- adjustment of gear ratios;
- adjustment of electronic systems.
The torque of the car will not change much from such actions; the power will increase, but only slightly.
Radical methods can come to the rescue, allowing those who wish to carry out in-depth tuning.
It consists in selecting a special crankshaft to replace the factory unit. This will allow you to change the car, practically reduce the ground clearance, and increase power. After all the necessary elements have been replaced, the vehicle as a whole is repaired and debugged.
Chip tuning is a relatively new modernization method that allows you to change parameters without mechanical intervention using special software. How much the engine weighs and when it was produced does not matter. The system will cope with any, even the most difficult, circumstances.
Replacing the ignition system belongs to the category of progressive tuning techniques. The best solution is a block called non-contact and allows you to significantly gain in power.
Experimenting with your own car is, of course, good, however, when deciding on the next modification, you need to think about whether they will be the last thing that the vehicle will finish off . The range of experiments is wide, so there is no need to rush. It’s better to think carefully and choose what will really come in handy.
Injection modification
The first in the line of internal combustion engines from the manufacturer AvtoVAZ, the 2106 engine received tuning in the form of distributed injection. At the same time, the owners got a headache:
- intense heating, since the mixture is scarce, the manufacturer’s cooling system cannot cope with temperature loads;
- increase in fuel consumption to 13 l/100 km in winter.
A positive point is the small budget for major repairs, within 10,000 rubles.
What we managed to significantly improve
Improved characteristics of the VAZ 2106:
- Using a new cylinder block of improved design with a changed diameter.
- The VAZ 2106 engine has increased power due to an increase in the total volume of the power unit and improved characteristics and properties of the cylinders.
- The use of new gaskets due to changes in cylinder diameters.
- Equipped with pistons with a diameter of 79 mm, borrowed from the eleventh model.
- Ensuring uniform heating of the pistons thanks to cylindrical wells in the motor and the use of steel temperature control plates on the pistons.
The most common breakdowns of the sixth engine
Car owners most often encounter the following defects in engine operation:
- The internal diameter of the cylinder increases by 0.15 mm after traveling more than 5 thousand km. This defect occurs if the engine lubricant is not replaced in a timely manner.
- The camshaft is worn out.
- Sound effects in the form of tapping in the engine. This defect can be eliminated by adjusting the valves and replacing the fuel with higher octane fuel. If these measures do not help, then you need to contact the nearest service station, where the pistons and connecting rod bearings will be diagnosed and repaired.
- Oil pressure drops. In this case, the lubricant does not reach the rubbing surfaces, as a result of which the friction force increases, causing the gaskets to burn out, accelerated wear of the working parts, and the device becomes unusable.
- Creaks indicate a breakdown in the timing chain tensioner, damper or pump bearing.
- If the engine stalls while driving, you need to look into the ignition or power systems.
- The engine turns off at idle when there is a failure in the idle speed or air damper adjustments.
- Engine trouble, with this defect it is necessary to adjust or replace burnt valves and cylinder head gasket. The cause of tripling can also be fuel with a low octane number.