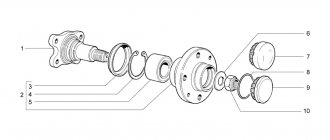
Car rear wheel bearings are a type of bearing support that ensures the rotation of the rear wheel of a car and its rigid fixation on the axle. The bearing itself is located in the hub, to which the wheel is in turn attached. Bearings differ in design, size, and technical characteristics.
In this article we will consider the following questions:
- Methods for replacing rear wheel bearings;
- Causes and symptoms of malfunction;
- Types of wheel bearing units, numbers and sizes;
- Tips for use and replacement.
To begin with, we present 2 typical layouts of parts. In the diagram on the left is a non-separable hub assembly with HUB-3 (3rd generation bearing) - on the right is HUB-1 (1st generation).
The main signs of wheel bearing failure
There are the following signs by which you can recognize that there is a malfunction in the wheel bearing:
- The occurrence of wheel play, no matter what - lateral or along the axle. This problem can be accompanied either by uneven wear of the tire tread, or when driving straight, the car constantly moves to the side, or the steering wheel begins to beat, as is the case with insufficiently correct wheel balancing;
- The presence of a hum (noise) in the hub area that changes its tone depending on the speed at which the car is moving. Due to inexperience, drivers may attribute such sounds to violations in wheel alignment adjustments or attribute them to a special reaction of the tire treads.
How to determine when an element is time to change?
The main signs of a wheel bearing malfunction are a metallic hum and/or wheel play while driving. The last criterion is difficult to notice on your own. A video taken from a car behind you may help.
In order for the driver to determine where the fault is located, it is necessary to turn sharply at speeds of up to 15 km/h. If the noise disappears, the element on the opposite side has broken. To check, it is recommended to make a similar turn in the other direction.
When grinding and crunching noises are heard, the driver is advised to stop. This is a sign of complete failure of the bearing, which may result in the wheel flying off.
In stationary conditions, the malfunction is determined after the vehicle is placed on a lift. Deviations on the drive axles are checked by accelerating to 70 km/h and listening to the hum near each of the wheels. If the wheel is not driving, it is turned by hand and rocked. The play will be felt.
Correct wheel bearing diagnosis
The sequence of actions must correspond to the following algorithm:
- The wheel to be diagnosed is removed so that it can rotate freely. In this case, the car is either placed on a lift, or a working jack is used;
- You have to spin the wheel to make it clear. That its rotation is free. There are cases where noise occurs, the cause of which is insufficient brake release of the wheel, while well pads rub against the drum or disk;
- You need to rock the wheel, taking it by both edges, upper and lower, both towards you and away from you. After which the procedure is resumed after a ninety-degree turn is made.
When play is detected, a check is made to see how the hub nuts are tightened. This is where a large-levered crank comes in handy. In addition to being designed to withstand high forces, the size of its socket head is considered to be the most suitable.
You will also need a technical specification for automotive equipment indicating the tightening torque for the bearing nut.
Actions are carried out in the following sequence:
- The nut cap is removable for protection;
- If there is a cotter pin, it must be removed;
- While driving, an assistant must press the brake device to secure the wheel;
Using a prepared wrench, the tightening torque force is checked. If the bearing meets specifications but there is still play, the bearing must be replaced.
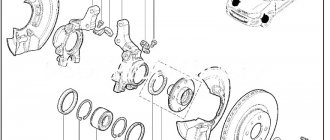
Replacing the hub bearing on the front axle
The general algorithm is the same, with the exception of features in the design of the car:
- The battery device is switched off;
- The bolts on the wheel are loosened;
- Using a lift or shoes with a jack, the front wheel is raised;
- The protective cap at the hub nut is compressed. Then the hose is removed from the drive shaft, more specifically from the threaded cap;
- After the assistant presses the brake, the nut on the hub is unscrewed;
- The wheel is removed;
- The brake caliper is unscrewed from its mounting location so as not to damage the hoses. The part is carefully secured to the body with wire. The hoses must remain free;
- The ABS sensor connector is disconnected;
- The disk is removed after unscrewing the screws;
- The steering tip is disconnected from the rack, then the same is done with the conical tip;
- The stand must be pulled slightly towards you to remove the splined part from the hub;
- Using a puller, you have to remove the hub and the bearing with it;
- The new set is pressed in. A separately made bearing is installed not in the old hub, but in the new one;
Assembly is carried out in reverse order.
Which way is better
There is no definite answer, because every repair is a special case. It all depends on the age of the car, the wisdom of the vehicle owner, and his responsibility for the technical condition of the car. If a person bought a car to ride and then sell the “tortured steel horse”, then the auto mechanic will have to work on such a car for quite a long time, almost all components of the system will be worn out. In this case, the second or third option is suitable. Ideal car repairs are carried out in a short time and do not require additional financial investments. The first method - the most professional and effective - is used by a car mechanic and will very quickly return the car to operation.
Thus, we have outlined three main ways to remove a bearing, but each craftsman chooses the most optimal one, that is, the one that is most suitable in a particular case. Good luck to everyone with their DIY repairs. If you are not sure, then contact a specialist.
An important part of a car's chassis is the wheel hub. For its free rotation on the axis, a bearing is placed in it. During operation, it wears out and the wheel bearing needs to be replaced. A signal that the wheel bearing is worn out can be a crunching sound, vibration, and the car deviating from the course when moving in a straight line.
Replacing the wheel bearing on the rear wheels
The operations are performed in the same way and in the same order as in the case of the front wheels.
The process differs as follows:
- There is no need to disconnect the tie rod;
- There is also no need to dismantle the CV joint;
- In the case of using a press with a lever suspension on the machine, the rack will not be dismantled, but the lever device with the hub will be carried out.
So the procedure in practice turns out to be simpler to perform.
Selection of ZPS
When choosing a rear wheel bearing, you should focus on the required characteristics and manufacturers who today produce ZPS suitable for the VAZ 2109.
Let's start with the characteristics. The choice should be made in favor of bearings with the following parameters.
| Characteristic | Index |
| Inner diameter | 30 millimeters |
| Outside diameter | 60 millimeters |
| Width | 37 millimeters |
| Weight | 0.4 kilograms |
| Bearing ball diameter | 9.525 millimeters |
| Number of balls in the bearing | 28 pieces |
For the rear hub, a ball, angular contact, double-row closed type bearing is used.
Now let's talk about manufacturers. There are several of them, each of which has its own characteristics.
| Bearing manufacturer | Peculiarities |
| VBF from the Volgograd plant | Motorists consider this bearing plant to be quite reliable and proven. An important advantage is that fakes from the Volgograd manufacturer are quite rare on the market. |
| Bearings of the Saratov plant - SPZ | A close option to the Volgograd plant, which is famous for its reliability and has impressive popularity among owners of domestic cars. There are a few more fakes |
| SPZ 4 | These are products of the same Saratov plant, only for budget consumers. Quite cheap bearings are characterized by less durability. Otherwise, there are no serious complaints about quality |
| 20 GPZ. Kursk plant | Nowadays it is very rare to come across products from this plant, since the company produced bearings back in the days of the USSR and for some time after the cessation of its existence. Today there is no production, but occasionally the remains of bearings can be found. The quality is excellent (USSR, after all), but the shutdown of production will not allow you to easily find it. Maybe they are no longer anywhere at all. |